Underground drain pipes come in various materials including PVC, ABS, cast iron, HDPE, clay, concrete, and copper. Standard residential sizes range from 110mm to 300mm diameter, while commercial applications may require larger dimensions. Installation requires proper slope and bedding, with maintenance essential for preventing blockages and damage. Regular inspections can identify issues early, while repairs or replacements depend on pipe age and condition. Understanding these components guarantees peak drainage system performance.
Key Takeaways
- Common underground drain pipe materials include PVC, ABS, cast iron, HDPE, clay, concrete, and copper, each with specific benefits and applications.
- Standard residential pipe sizes range from 110mm to 300mm, while commercial applications typically use larger diameters above 12 inches.
- Proper installation requires gravel-filled trenches with a minimum slope of 1/4 inch per foot for effective drainage performance.
- Regular maintenance through hydro jetting, snaking, or chemical treatments prevents clogs and extends pipe system longevity.
- Replacement is necessary for pipes over 50 years old or with structural damage, while minor issues can be repaired through relining.
Understanding Underground Drain Pipes & Drainage Systems
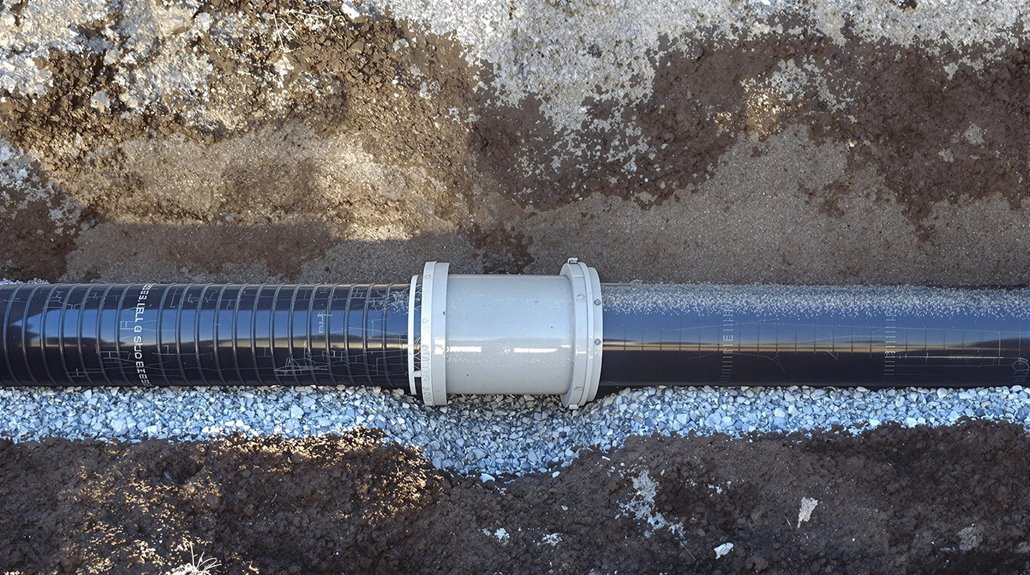

Underground drain pipes form the backbone of modern drainage infrastructure, serving as crucial conduits for directing water away from buildings and preventing potential flooding issues.
These drainage systems utilize various types of underground drainage pipes, with materials ranging from traditional clay to modern PVC, each offering specific advantages in corrosion resistance and durability.
Key components of effective underground drainage systems include:
- Appropriate pipe sizes, typically 4 inches for residential applications
- Proper slope gradients of 1-2% to guarantee ideal water flow
- Strategic placement and connection points for maximum drainage efficiency
Regular maintenance of underground drainage pipes is essential for preventing system failures and extending service life.
When issues arise, prompt repair or replacement becomes necessary to maintain system integrity.
Modern materials like PVC have revolutionized drainage systems by offering superior performance characteristics and easier installation compared to traditional materials, making them the preferred choice for both new installations and replacements.
Common Materials Used In Underground Drainage Pipes

Underground drainage systems utilize various materials engineered to meet specific performance requirements and site conditions. The selection of pipe material impacts vital factors including durability, chemical resistance, installation complexity, and system longevity. Modern drainage installations commonly incorporate materials such as PVC, ABS, cast iron, HDPE, clay, concrete, and copper, each offering distinct advantages for particular applications.
| Material Type | Primary Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PVC/ABS | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Residential systems, general drainage |
| Cast Iron | High strength, fire-resistant | Commercial buildings, stack lines |
| HDPE | Flexible, root-resistant | Exterior drainage, agricultural use |
| Clay/Concrete | Chemical stability, compression strength | Municipal systems, heavy load areas |
| Copper | Biostatic properties, heat resistant | Special drainage, high-temperature waste |
PVC & ABS Underground Drainage Pipes
UPVC underground drainage pipes represent a specialized variant of PVC piping, featuring enhanced rigidity and structural integrity for subterranean applications.
The material's superior chemical resistance and UV stabilization properties make it particularly suitable for long-term underground installations.
UPVC pipes maintain excellent flow characteristics due to their smooth internal surfaces, while their joint systems guarantee reliable, watertight connections essential for underground drainage networks.
UPVC Underground Drainage Pipes
Modern drainage systems heavily rely on UPVC pipes, which are manufactured through extrusion molding using unplasticized polyvinyl chloride.
These underground drainage pipes feature high strength and chemical resistance, with diameters ranging from 110mm to 300mm for residential and commercial applications.
Their smooth internal surfaces prevent clogs while ensuring maximum flow efficiency.
UPVC pipes boast an expected lifespan exceeding 50 years when installed underground.
Cast Iron Underground Drainage Pipes
Cast iron drainage pipes represent one of the most durable and time-tested materials in underground plumbing systems. Their exceptional durability enables them to withstand significant external pressures, making them particularly suitable for heavy-load areas.
These underground drainage pipes offer superior fire resistance and can endure high temperatures, ensuring reliable performance in diverse installation environments.
While cast iron pipes boast impressive longevity, often exceeding 50 years of service, they remain susceptible to corrosion and oxidation over time. Regular inspections are essential for maintaining system integrity, and eventual replacement may be necessary.
Installation costs tend to be higher due to their substantial weight, though this mass provides excellent noise reduction properties. Despite higher installation expenses, their sound-dampening qualities and robust durability make them a preferred choice for residential drainage applications.
Corrugated Or Perforated HDPE Underground Drainage Pipes
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) drainage pipes, particularly in their corrugated and perforated variations, represent a versatile solution for underground water management systems.
The corrugated design enhances structural integrity while maintaining a smooth interior surface that facilitates peak flow characteristics. These HDPE pipes feature strategic perforations that enable efficient water infiltration, making them ideal for applications such as French drains and leach fields.
Available in diameters ranging from 4 to 12 inches, these pipes accommodate both residential and commercial drainage requirements.
Their lightweight nature simplifies installation across diverse terrain conditions, while their chemical resistance guarantees extended longevity in challenging soil environments.
During replacement projects, HDPE's durability and adaptability make it a preferred choice, particularly when dealing with aggressive groundwater or chemical-laden runoff conditions.
Clay & Concrete Underground Drainage Pipes
While HDPE pipes offer flexibility and lightweight installation, traditional clay and concrete drainage pipes remain stalwart options in underground infrastructure.
Clay drainage pipes excel in resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation, making them ideal for industrial sewer lines and complex plumbing issues. Their inert properties guarantee long-term reliability in challenging environments.
Concrete drainage pipes demonstrate superior strength for heavy-duty applications and effectively manage groundwater flow. Modern concrete technology has enhanced their capability to meet increasing structural demands of contemporary drainage systems.
Both materials provide exceptional temperature resistance and durability, though they require specialized installation techniques.
While clay pipes maintain their historical significance, concrete drainage pipes have gained prominence in new underground drainage pipe installation projects due to their advanced engineering properties and robust construction characteristics.
Copper Underground Drainage Pipes
Among underground drainage materials, copper pipes represent a premium option characterized by exceptional durability and natural antimicrobial properties.
These copper underground drainage pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and typically maintain functionality for over 50 years, though their performance may diminish in highly acidic or alkaline soil conditions.
While their malleability enables flexible installations and adaptable configurations, copper pipes command considerably higher costs compared to alternative materials.
The installation process requires specialized skills for soldering or brazing joints, further increasing overall expenses.
Despite these considerations, copper's inherent antimicrobial properties make it particularly valuable for specific applications where bacterial control is essential.
Although less commonly used for standard drainage systems due to cost factors, copper remains a reliable choice where premium performance and longevity justify the investment.
Slotted Underground Drainage Pipes
Specifically engineered with strategic perforations, slotted underground drainage pipes serve as vital components in water management systems by facilitating controlled water infiltration and dispersal.
These specialized pipes, commonly manufactured from PVC and HDPE materials, effectively manage water accumulation in areas prone to saturation.
Available in diameters ranging from 4 to 12 inches, these drainage solutions offer versatility for various applications.
Installation typically involves placing the pipes in gravel-filled trenches, optimizing water collection and distribution capabilities.
The combination of perforated design and surrounding aggregate guarantees efficient drainage performance while preventing soil erosion.
PVC options provide superior corrosion resistance and straightforward installation, while HDPE alternatives offer enhanced flexibility and durability.
This infrastructure plays an important role in protecting structures and landscaping by directing excess water away, greatly reducing flooding risks.
Flexible Underground Drainage Pipes
Modern flexible underground drainage pipes represent a significant advancement in drainage system technology, utilizing materials such as PVC, HDPE, and polyethylene to provide superior adaptability during installation.
These materials excel in chemical resistance and demonstrate remarkable resilience against root intrusion, ensuring long-term system integrity.
The flexibility of these drainage systems allows for efficient maneuvering around underground obstacles, reducing the need for additional fittings and simplifying installation processes.
Standard sizes ranging from 4 to 12 inches in diameter accommodate various drainage requirements.
When properly installed, PVC and HDPE pipes offer impressive durability, with expected lifespans between 50 to 100 years.
However, environmental factors, including soil composition, temperature fluctuations, and ground movement, can impact their longevity and performance.
Standard Sizes & Dimensions For Underground Water Drainage Pipes & Fittings
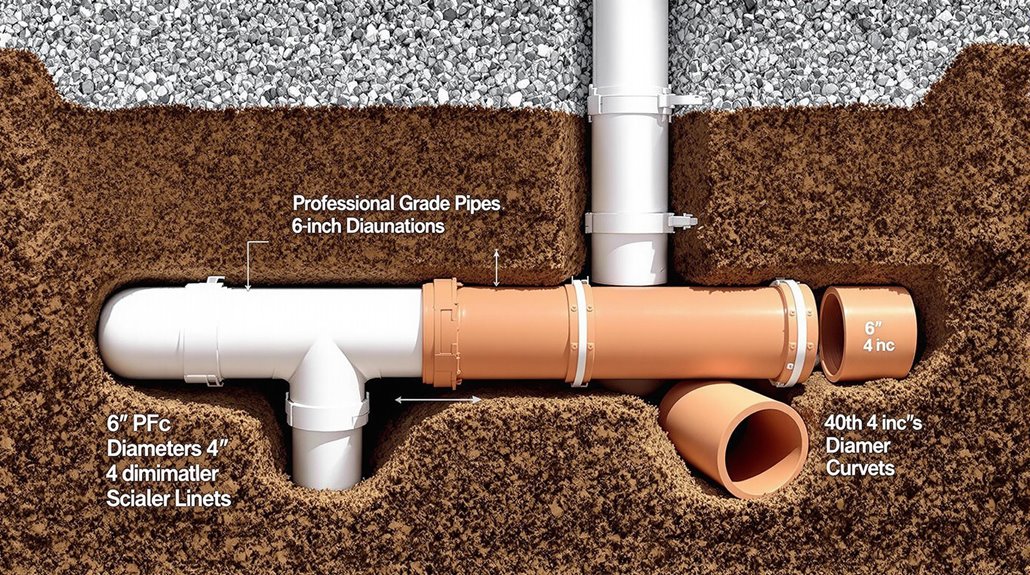

Underground drainage pipes adhere to standardized dimensions, with residential systems typically utilizing 4-inch and 6-inch diameter pipes, while commercial applications may require larger 8-inch to 12-inch diameters based on flow requirements.
The selection of appropriate pipe sizes depends on calculated water volumes, required slope gradients (typically 1/4 inch per foot minimum), and local building codes that specify main line categories.
Proper sizing guarantees ideal flow capacity, with engineers utilizing specific flow rate calculations that account for factors such as catchment area, rainfall intensity, and system design parameters.
Residential Pipe Size Standards
Underground drainage systems utilize standardized pipe sizes to guarantee compatibility and proper flow characteristics across residential installations. The most common pipe diameters in residential applications include 110mm, 150mm, 160mm, and 225mm, each serving specific drainage requirements from household waste to stormwater management. These standardized dimensions facilitate proper fitting selection and enable efficient system design that complies with local building regulations.
| Pipe Diameter (mm) | Typical Application |
|---|---|
| 110 | Domestic waste and soil pipes |
| 150 | Secondary drainage lines |
| 160 | Main sewer connections |
| 225 | Large-scale drainage and storm systems |
160mm Underground Drainage Pipes & Fittings
Standard residential drainage systems utilize specific pipe dimensions that conform to established industry specifications.
Common mm underground drainage pipe sizes range from 50mm to 300mm, with 110mm and 160mm being typical.
PVC and flexible corrugated materials are preferred for underground drainage pipe repair and replacement.
Underground drainage pipe fittings must comply with local building codes and maintain a minimum slope of 1-2%.
110mm Underground Drainage Pipes & Fittings
Residential drainage systems rely on standardized pipe dimensions that conform to established industry specifications.
Underground drainage pipe sizes typically range from 50mm to 150mm in diameter, with PVC and ABS materials chosen for their corrosion resistance.
Standard fittings for underground drainage, including couplers and bends, match specific pipe dimensions to guarantee maximum flow capacity and proper installation.
225mm Underground Drainage Pipes & Fittings
The dimensions and specifications of underground drainage pipes adhere to established industry standards that guarantee consistent performance across residential installations.
Standard mm underground drainage pipes range from 50mm to 300mm, with 110mm underground drainage pipe being most common.
PVC drainage pipes and drainage fittings are manufactured with precise internal diameters, ensuring sizes matching throughout the system to maintain drainage capacity, efficient water runoff, and prevent flooding per regulations.
150mm Underground Drainage Pipes & Fittings
Underground drainage pipe dimensions adhere to standardized measurements across residential and commercial applications, with diameters typically ranging from 50mm to 300mm.
Residential underground drainage commonly utilizes 100mm and 150mm pipe sizes to guarantee adequate flow capacity.
PVC and ABS pipes, valued for their corrosion resistance, connect via typical fittings including couplers and inspection chambers.
Local building codes regulate these specifications for proper installation.
Commercial Drainage Size Guide
Commercial drainage systems require standardized pipe dimensions to verify proper water flow and system compatibility across various applications. Underground drainage pipe specifications typically range from 4 to 12 inches in diameter, with materials including PVC, cast iron, and HDPE selected based on specific project requirements. Proper pipe size selection verifies peak flow rates and prevents system overload.
| Pipe Type | Standard Diameter (inches) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | 4-6 | Light Commercial |
| HDPE | 6-8 | Medium Commercial |
| Cast Iron | 8-12 | Heavy Commercial |
Standard pipe fittings complement these dimensions, facilitating proper connections and direction changes. The selected diameter must accommodate peak water flow while maintaining a 1-2% slope for effective drainage. Regular inspection and repair of these components verify sustained system performance.
Slope & Diameter Requirements
Proper sizing and slope requirements for drainage pipes remain critical factors in designing effective underground water management systems. Standard residential underground drainage pipes typically range from 4 to 6 inches in diameter, while commercial applications often require larger dimensions to handle increased water flow. A minimum slope of 1% guarantees proper drainage and prevents system failures.
| Application Type | Minimum Diameter | Recommended Slope |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | 4 inches | 1/8" per foot |
| Commercial | 6 inches | 1/4" per foot |
| Stormwater | 4-8 inches | 1-2% grade |
| Heavy Soil Areas | 6+ inches | 2%+ grade |
| Industrial | 8+ inches | Site-specific |
Local building codes govern specific requirements for underground drainage pipe installations, with particular attention to diameter and slope specifications for rainwater and stormwater management. Soil conditions may necessitate adjustments to these standard parameters.
Main Line Size Categories
Standard drainage pipe systems utilize specific size categories to guarantee ideal flow capacity and system compatibility across various applications. Underground drainage pipe installations commonly feature PVC and HDPE materials in standardized dimensions, offering superior water management capabilities and resistance to corrosion. These materials, available in various standard sizes with matching pipe fittings, facilitate efficient repair and replacement procedures.
| Size Category | Common Applications | Flow Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 4-inch | Residential | Low-Medium |
| 6-inch | Commercial | Medium |
| 8-inch | Industrial | High |
| 10-inch+ | Municipal | Very High |
These standardized dimensions ensure consistent performance across drainage systems while maintaining compatibility with existing infrastructure, making maintenance and system modifications more straightforward.
Capacity & Flow Calculations
Determining the correct pipe dimensions and flow calculations serves as a critical foundation for effective underground drainage system design. Residential plumbing systems typically utilize underground drainage pipes ranging from 3 to 12 inches in diameter, with 4-inch and 6-inch being most common. Flow capacity calculations employ Manning's equation, considering pipe diameter, slope, and liquid characteristics for ideal gravity-assisted flow.
| Pipe Type | Diameter (inches) | Flow Capacity (GPH) |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | 4 | 2,200 |
| PVC | 6 | 5,000 |
| Clay | 4 | 1,800 |
| Clay | 6 | 4,200 |
Flow efficiency depends on proper pipe diameter selection, maintaining appropriate fittings, and preventing clogging. Engineers consider expected flow volume and system requirements when specifying types of pipes to guarantee long-term performance and minimal maintenance requirements.
Commonly Used Underground Drainage Pipe Fittings
Underground drainage systems incorporate several essential fittings designed to connect pipe sections and facilitate water flow directionally. Standard sizes for drainage pipe fittings typically align with pipe diameters, ranging from 3 to 12 inches. PVC fittings and ABS fittings dominate installations due to their corrosion resistance and compatibility with solvent cement joining methods.
| Fitting Type | Primary Function | Standard Sizes |
|---|---|---|
| Couplings | Join straight sections | 3" – 12" |
| Tees | Create branch lines | 3" – 12" |
| Elbows | Change flow direction | 3" – 12" |
| End Caps | Terminate lines | 3" – 12" |
Local building codes regulate fitting specifications, ensuring secure connections and superb water flow. Most modern fittings feature smooth interior surfaces and integrated gaskets, maximizing system efficiency while minimizing potential leakage points.
Signs Of Underground Pipe Damage & Deterioration
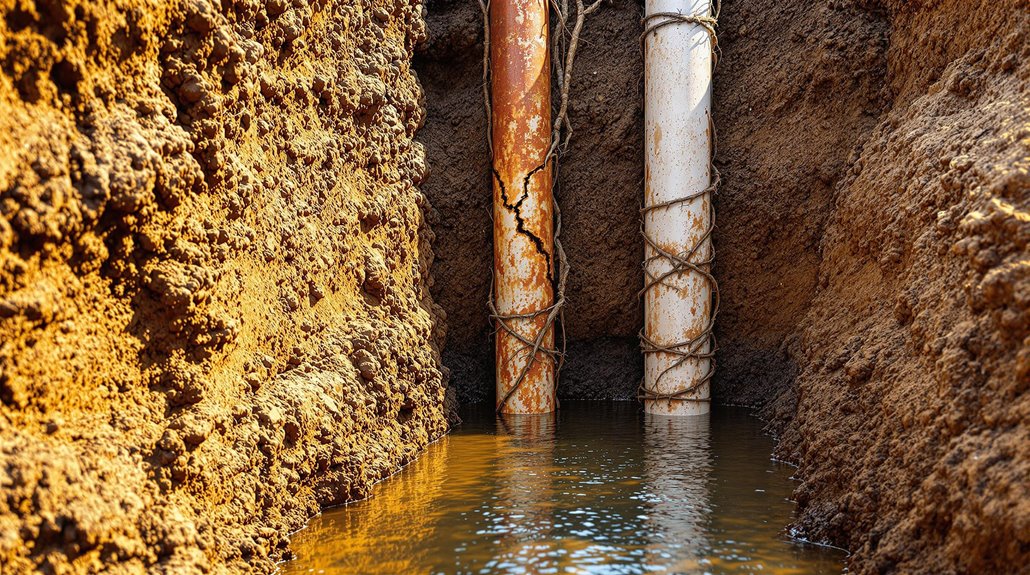

Recognizing the early warning signs of pipe damage and deterioration can prevent costly repairs and potential property damage. Property owners should monitor for persistent slow drainage, foul odors emanating from the ground, and visible pooling of water in yard areas. These indicators often signal underlying issues with underground drainage pipes.
| Sign | Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Drainage | Blockage/Damage | Reduced Flow Efficiency |
| Foul Odors | Pipe Breaks/Leaks | Sewage Contamination |
| Water Pooling | Structural Failure | Soil Saturation |
| Root Infiltration | Cracked Pipes | System Blockage |
| High Water Bill | Hidden Leaks | Resource Waste |
Regular inspection can reveal corrosion in metal pipes, evidenced by rust stains in surrounding soil. Cracked pipes frequently lead to root infiltration, causing systematic deterioration and frequent backups in household plumbing. Unexplained increases in water bills, despite consistent usage patterns, typically indicate underground leakage requiring immediate professional assessment.
Essential Maintenance Practices For Drain Pipes
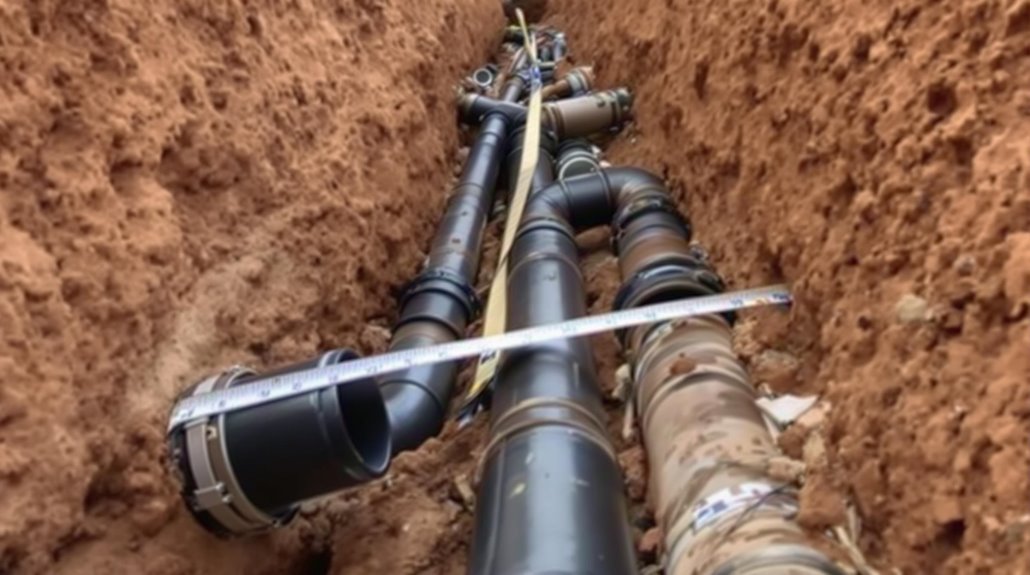

Maintaining underground drain pipes requires a systematic approach to prevent costly repairs and system failures. Regular inspections help identify signs of leaks, deterioration, or damage before they escalate into major plumbing emergencies.
Professional drain cleaning services should be scheduled periodically to remove accumulated debris and maintain peak flow through the system.
Essential maintenance practices include:
- Monitoring proper drainage slope of 1-2% to prevent water stagnation
- Implementing root barriers around clay or metal pipes to prevent intrusion
- Conducting routine inspections for wet spots or drainage backups
For older materials like Orangeburg or clay, replacement with modern PVC or HDPE pipes may be necessary to guarantee long-term system reliability.
Underground drainage pipe maintenance should also include documentation of pipe age, material type, and repair history. This information proves valuable when planning future upgrades or addressing emerging issues in the plumbing system.
Professional Repair Methods & Techniques
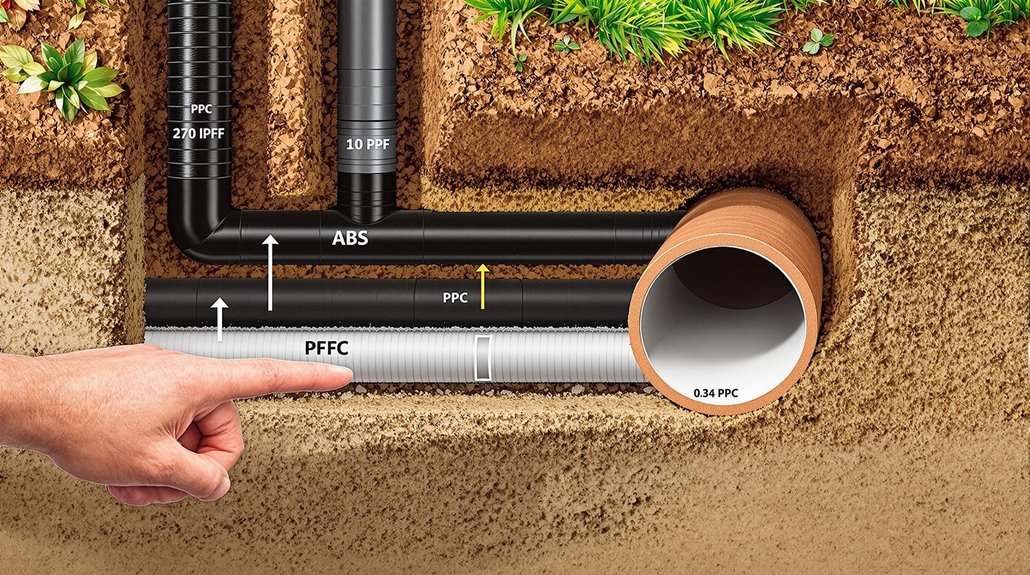

Professional repair methods for underground drain pipes have evolved considerably with advancements in technology and materials science. Trenchless technology now enables repairs with minimal surface disruption, while video inspection technology allows precise diagnosis of underground drainage pipe issues. Pipe relining has emerged as a cost-effective solution, inserting new linings into existing pipes to restore functionality.
| Method | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pipe Relining | Damaged Pipes | Minimal Excavation |
| Video Inspection | Diagnostics | Precise Assessment |
| Full Replacement | Severe Damage | Long-term Solution |
When complete replacement becomes necessary, professionals typically recommend PVC or ABS materials for their superior durability and resistance to corrosion. All repair and replacement work must comply with local building codes, making professional expertise essential. These modern repair methods guarantee efficient restoration of drainage systems while minimizing property disruption, ultimately extending the service life of underground infrastructure.
When To Replace Vs. Repair Underground Pipes
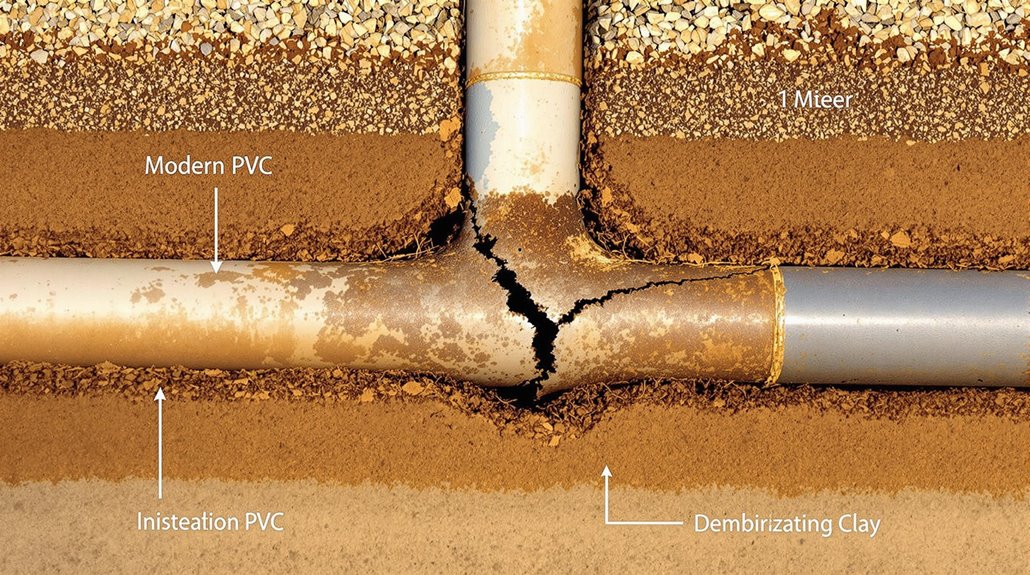
Making an informed decision between pipe replacement and repair requires careful evaluation of multiple factors, including pipe material, age, and extent of damage. Underground drainage pipe replacement becomes necessary when materials like clay or Orangeburg show signs of deterioration after 50-70 years of service.
| Condition | Replace | Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Age | >50 years old | <50 years old |
| Damage Type | Structural failure | Minor cracks |
| Frequency | Recurring issues | One-time problems |
| Cost Impact | Multiple repairs needed | Single repair sufficient |
Significant corrosion, root infiltration, or cracked joints detected during camera inspections often warrant complete replacement rather than repeated repairs. When pipes exhibit structural issues such as sagging or warping, replacement prevents potential property damage. While routine maintenance can extend pipe materials' lifespan, persistent leaks and blockages in aging systems indicate replacement as the most cost-effective solution. Professional assessment helps determine whether repair or replacement will provide the best long-term outcome.
Underground Drainage Pipe Price Factors

Underground drainage pipe costs encompass three primary financial considerations that property owners must evaluate.
The initial assessment includes repair expenses, which typically range from $150-$600 for minor fixes, while complete replacements can exceed $7,000 depending on pipe material and accessibility.
Installation costs vary considerably based on several key factors:
- Labor rates and complexity of installation requirements
- Type and diameter of pipe material selected
- Site conditions and local permit requirements
Average Underground Drain Pipe Repair Costs
Repairing drain pipes beneath the soil surface involves several key cost factors that property owners should consider. Video camera inspections, ranging from $100 to $300, provide essential diagnostic information before repair work begins. Labor costs typically range from $50 to $150 per hour, while materials such as PVC or ABS pipes cost between $0.50 and $3.00 per foot. Excavation work adds $1 to $5 per square foot to overall expenses.
| Cost Component | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Labor (hourly) | $50-$150 |
| Materials (per foot) | $0.50-$3.00 |
| Excavation (sq ft) | $1-$5 |
| Complete Replacement | $2,000-$15,000 |
Severely damaged pipes requiring complete replacement can escalate costs markedly, potentially reaching $15,000. Homeowners insurance may cover certain types of pipe damage, making it essential to review policy coverage before initiating repairs.
Average Underground Drain Pipe Replacement Costs
The cost of replacing underground drain pipes varies greatly based on multiple factors, with total project expenses typically ranging from $2,500 to $15,000. Material selection greatly impacts project costs, with PVC pipes costing $0.50-$2.00 per foot and cast iron pipes ranging from $4.00-$10.00 per foot. Labor charges for underground drainage pipe installation typically add $40-$150 per hour to the total expense.
| Cost Component | Price Range |
|---|---|
| PVC Pipes | $0.50-$2.00/ft |
| Cast Iron Pipes | $4.00-$10.00/ft |
| Labor Rates | $40-$150/hour |
| Total Installation | $50-$200/linear ft |
Home insurance may cover pipe replacement costs when damage results from sudden events rather than gradual deterioration. Factors affecting final costs include water line depth, soil conditions, accessibility, and local building regulations.
Average Underground Drain Pipe Installation Costs
Installing home drainage pipes involves multiple cost variables that typically range from $2 to $6 per linear foot for materials alone, while complete system installation can reach $1,000 to $3,000 for residential properties. Professional installation increases total costs by 50-100%, reflecting labor and equipment requirements.
| Cost Factor | Price Impact |
|---|---|
| Pipe Diameter | $2-6/linear ft |
| Soil Conditions | 15-30% variance |
| Additional Components | $100-500 |
| Professional Labor | 50-100% increase |
| Landscape Restoration | $200-800 |
The final underground drainage pipe installation costs depend considerably on pipe materials selected, site-specific soil conditions, and required additional components such as fittings and drainage basins. Local permits, professional inspections, and necessary landscape restoration work contribute to the overall project expense, with regional variations affecting final prices.
Additional Cost Considerations That May Arise

When undertaking underground drain pipe projects, property owners should anticipate several additional expenses beyond basic material and labor costs. The need for excavation equipment and manual labor to access underground drainage pipes can greatly impact project expenses. Before repair or replacement work begins, blockage removal services like hydro-jetting may be necessary. Specialized fittings and adapters for connecting to existing systems further increase material costs.
| Cost Category | Description | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Excavation machinery rental | High |
| Labor | Skilled workers and operators | High |
| Cleaning | Hydro-jetting and blockage removal | Medium |
| Materials | Specialized fittings and adapters | Medium |
| Compliance | Building code requirements and permits | Variable |
Compliance with building codes often requires specific materials or experienced contractors, while disposal fees for old pipes and excavation debris contribute to the overall project budget. These additional considerations can considerably affect the final cost of underground drainage projects.
Soil Considerations & Environmental Impact

Successful underground drainage systems require careful evaluation of soil conditions and their potential environmental effects. The selection of appropriate pipe materials and installation methods depends heavily on soil type, with clay soils demanding enhanced moisture management and sandy soils allowing greater flexibility in pipe selection. Proper bedding and careful attention to soil compaction during installation are critical for system longevity.
Key environmental considerations include:
- Selection of sustainable pipe materials, such as recycled HDPE or corrugated pipes, to reduce carbon footprint
- Management of water runoff to prevent soil erosion and minimize water pollution
- Implementation of regular maintenance protocols to guarantee system integrity and prevent groundwater contamination
Underground drainage pipe systems must balance engineering requirements with environmental stewardship. This includes considering how the system affects local ecosystems, implementing proper installation techniques, and maintaining ongoing inspection schedules to prevent deterioration and maximize environmental protection.
Building Codes & Permit Requirements
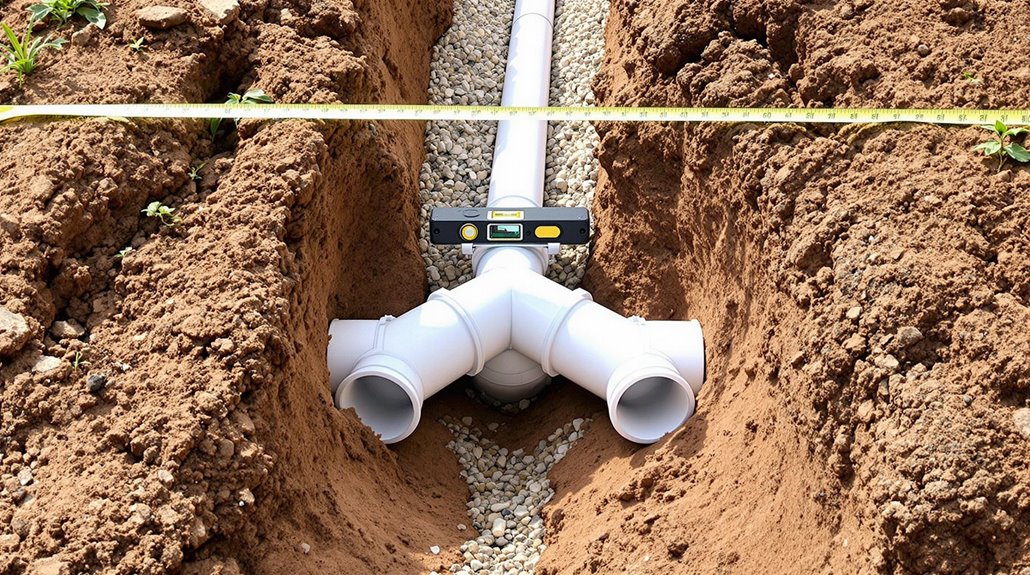

The complex framework of building codes and permit requirements plays an essential role in regulating underground drain pipe installations across jurisdictions. Local governments enforce specific regulations governing installation methods, minimum depth requirements, and system specifications to guarantee public safety and environmental protection. Compliance with these codes prevents sewage leaks, project delays, and costly fines.
| Regulatory Aspect | Requirements | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Methods | Technical specifications | System integrity |
| Depth Requirements | Minimum burial depths | Freeze protection |
| Distance Guidelines | Setbacks from structures | Environmental safety |
| Permit Processing | Documentation/approvals | Project timeline |
Before initiating any underground drainage project, contractors must obtain necessary permits and verify compliance with local building codes. These regulations often specify acceptable materials, installation techniques, and required distances from existing utilities and water sources. Adherence to these requirements not only guarantees legal compliance but also promotes system longevity and minimizes environmental impact.
Modern Technologies In Pipe Assessment & Repair
Modern advancements in pipeline assessment and repair technologies have revolutionized the underground drainage industry, enabling more precise diagnostics and efficient maintenance solutions. Video camera inspections provide detailed internal visualization of pipe conditions, while ground penetrating radar accurately locates underground drainage pipes without excavation. Trenchless technology minimizes surface disruption during pipe repairs, utilizing innovative methods like pipe bursting and slip lining.
| Technology | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Smart Sensors | Real-time monitoring of leaks and flow rates |
| Video Cameras | Internal pipe condition assessment |
| GPR Systems | Non-invasive pipe location detection |
| Robotic Units | Remote maintenance in confined spaces |
The integration of smart sensors and robotic technology has enhanced the industry's capability to detect and address blockages proactively. These automated systems navigate through complex pipe networks, performing maintenance tasks with unprecedented precision. This technological evolution has greatly reduced repair costs while improving the accuracy and efficiency of underground pipe assessments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Size Pipe for Underground Drainage?
Standard residential underground drainage requires 4-inch diameter pipes, while commercial applications utilize 6-12 inch pipes. Size selection depends on water volume, building codes, and specific site drainage requirements.
What Type of Pipe Is Used for Underground Sewers?
Underground sewers mainly utilize PVC and ABS pipes for their superior durability and corrosion resistance. Cast-iron, clay, and Orangeburg materials serve as alternatives, though modern installations favor plastic-based solutions.
What Are the 5 Types of Pipes?
The five primary pipe types include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), HDPE (high-density polyethylene), PEX (cross-linked polyethylene), cast iron, and copper, each offering distinct advantages for specific applications.
How Do You Fix a Broken Ground Drain Pipe?
While plumbers make it look easy, fixing broken ground pipes requires locating damage, careful excavation, cutting damaged sections, installing replacement pieces, and properly backfilling the excavated area.
Final Thoughts
Underground drainage systems represent a critical infrastructure investment, with studies indicating that up to 40% of residential sewer laterals may require replacement within the next decade due to aging materials and environmental stress. Understanding pipe materials, maintenance requirements, and replacement options is essential for property owners and contractors to guarantee system longevity and prevent costly failures. Modern assessment technologies and proper maintenance protocols greatly extend service life and reduce environmental impact.
For homeowners experiencing property damage related to underground drainage systems and filing insurance claims, insurance industry professionals and legal experts strongly advise consulting a qualified state-licensed public adjuster. Public adjusters work exclusively for policyholders, not insurance companies, serving as dedicated advocates throughout the claims process. These state-licensed professionals help navigate complex insurance policies, identify hidden damages often unknown to policyholders, thoroughly document losses, and negotiate with insurance companies to secure fair settlements while protecting policyholder rights.
The assistance of a public adjuster can lead to maximized claim payouts, expedited processing, and reduced stress during the claims process, allowing homeowners to focus on property restoration. Policyholders seeking expert guidance with their property damage claims can request a no-obligation free consultation with a Public Claims Adjusters Network (PCAN) member public adjuster through our contact page.








