Brush fires ignite in dry vegetation, such as shrubs and grasses, primarily due to human activities and natural sources. Unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and improper debris burning are common human causes, accounting for 84% of U.S. brush fires. Natural ignitions stem from lightning strikes or volcanic activity. Factors like drought, high temperatures, and strong winds exacerbate the spread and intensity. Equipment malfunctions and arson also contribute. Understanding these details is essential for effective fire prevention and safety strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Brush fires ignite in dry vegetation like shrubs and grasses, often due to human activities.
- Human causes, including unattended campfires and improper debris burning, account for 84% of U.S. brush fires.
- Natural causes like lightning strikes and volcanic eruptions can ignite dry vegetation.
- Environmental conditions such as drought, high temperatures, and strong winds enhance fire risk.
- Equipment malfunctions and arson also significantly contribute to brush fire ignitions.
Understanding the Basics of Brush Fires
When examining the fundamentals of brush fires, it is essential to recognize that these wildfires primarily ignite in dry vegetation such as shrubs and grasses, which serve as effective fuel sources during warm and arid conditions.
Human causes, particularly unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and intentional arson, are responsible for approximately 84% of these fires in the U.S. Such activities greatly increase the risk of ignition in areas with susceptible dry vegetation.
Conversely, natural ignitions, primarily from lightning strikes, account for a smaller portion, though they are most frequent during summer months when dry conditions prevail.
Weather conditions, including high temperatures and low humidity, exacerbate the flammability of dry vegetation, facilitating rapid wildfires spread. Wind further intensifies brush fire dynamics, potentially propelling flames at speeds up to 14.27 miles per hour.
Understanding these dynamics is vital for developing effective fire prevention and mitigation strategies.
Environmental Conditions Contributing to Brush Fires
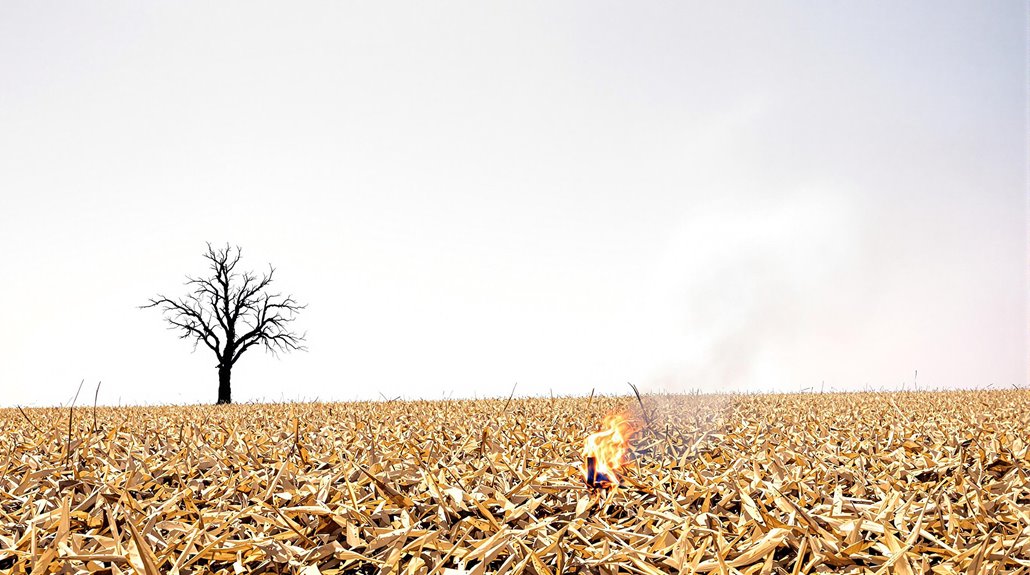

Although brush fires can occur under various circumstances, certain environmental conditions greatly elevate their likelihood and intensity.
Foremost among these are drought conditions, which lead to dry vegetation with low moisture content, rendering it highly flammable. High temperatures and low humidity further exacerbate the risk, creating an ideal environment for rapid ignition and combustion.
Strong winds play a critical role by supplying additional oxygen and dispersing embers, thereby accelerating fire spread and increasing the potential for ignition over large areas.
Dense foliage, particularly those comprising resinous plants, contributes considerably to the intensity and speed of fire spread. Importantly, certain seasons, such as late fall and early winter, are particularly susceptible to these conditions in regions like North Carolina.
The following factors are critical in understanding brush fire dynamics:
- Dry vegetation and flammable materials.
- High temperatures and low humidity.
- Strong winds facilitating fire spread.
- Dense foliage and vegetation types.
Common Human Activities Leading to Ignition
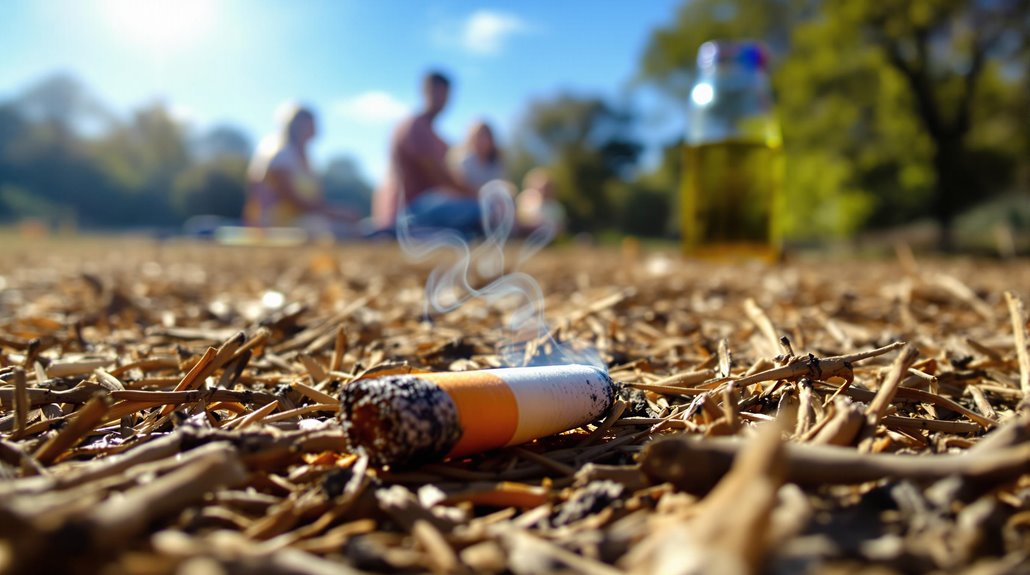

Due to various human activities, the risk of brush fire ignition considerably increases. Unattended campfires pose a significant threat as embers can ignite surrounding dry vegetation if not monitored. Similarly, burning debris without adherence to safety protocols can result in uncontrolled brush fires, particularly in hot, windy conditions. Equipment malfunctions, such as sparks from vehicles or machinery, contribute to approximately 11% of U.S. wildfires, emphasizing the importance of careful handling. Discarded cigarettes are another prevalent cause; when thrown from vehicles or carelessly dropped, they can readily ignite dry brush and grass. Arson remains a significant human-caused ignition source, responsible for about 21% of wildfires, demonstrating the danger of intentional fire-setting. Creating a 30-foot defensible space around properties by removing flammable vegetation significantly reduces the risk of brush fires spreading to structures.
| Human Activity | Risk Factor | Percentage Involvement |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Malfunctions | Sparks and Heat Sources | 11% |
| Arson | Intentional Ignition | 21% |
| Discarded Cigarettes | Ignition of Dry Vegetation | Significant Contribution |
Understanding these activities is important for fire prevention.
The Role of Weather in Brush Fire Spread
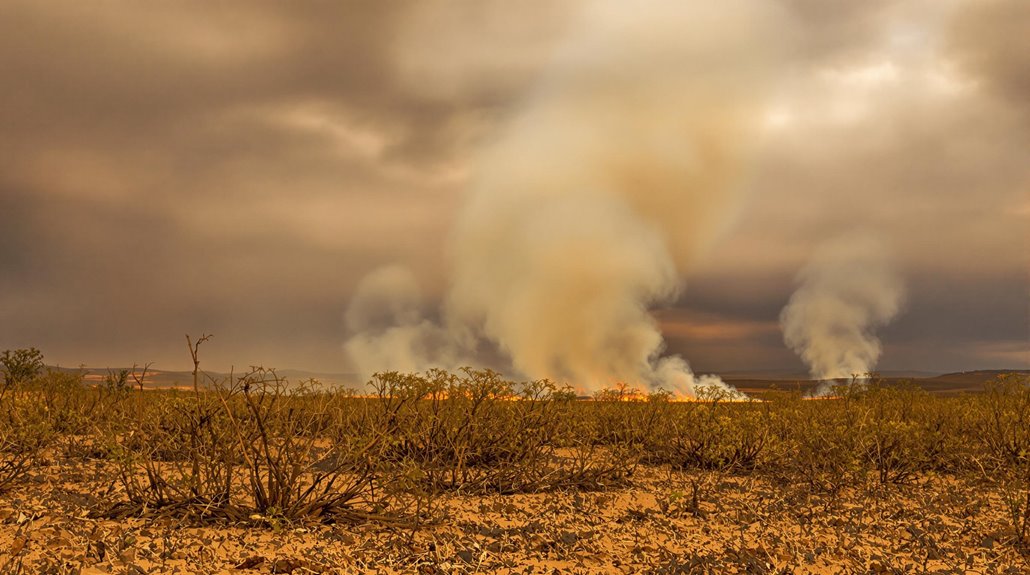

Weather conditions greatly influence brush fire behavior, with wind acting as a primary vector for fire spread by providing additional oxygen, carrying embers, and increasing flame intensity.
Elevated temperatures and reduced humidity levels enhance vegetation desiccation, thereby accelerating ignition and propagation.
Understanding these meteorological impacts is essential for effective fire management and safety planning in brush-prone regions.
Wind and Fire Intensity
The dynamics of wind greatly influence the behavior and intensity of brush fires. Wind acts as a catalyst, accelerating fire intensity and facilitating the rapid growth of brush fires. This occurs particularly under conditions of high temperatures and low humidity.
Wind contributes to fire behavior by:
- Increasing Spread Rate: Brush fires can travel up to 14.27 miles per hour due to strong winds.
- Carrying Embers: These embers ignite new fires, exacerbating the situation.
- Altering Fire Path: Sudden changes in wind direction lead to unpredictable fire behavior.
- Complicating Control Efforts: Wind-driven fires are challenging to manage, resulting in dangerous flare-ups.
Thus, understanding wind's role is essential for enhancing safety measures and effective firefighting strategies.
Temperature and Humidity Effects
While wind greatly influences brush fire dynamics, temperature and humidity also play critical roles in fire spread. High temperatures considerably reduce moisture content in dry vegetation, increasing its susceptibility to ignition.
Concurrently, low humidity levels exacerbate this condition by depleting moisture in both vegetation and air, enhancing flammability and accelerating fire spread. A relative humidity below 30% remarkably increases fire risk, as heat waves drive critical periods of fire danger.
Such weather patterns, particularly during late afternoon and early evening, create ideal conditions for brush fires to ignite and propagate swiftly. Understanding these factors is essential for predicting fire behavior and implementing effective safety measures to mitigate brush fire risks in susceptible regions.
Natural Causes of Brush Fires

Although often overshadowed by human activities, natural causes play an essential role in the ignition of brush fires. Understanding these causes is vital for fire prevention and safety.
Natural causes include:
- Lightning Strikes: Responsible for many wildfires, particularly during the summer months, lightning can ignite dry vegetation, leading to widespread fires.
- Volcanic Eruptions: Molten lava and hot ash from eruptions can ignite flammable materials, creating a fire hazard in nearby brush-covered areas.
- Spontaneous Combustion: This occurs when decomposing organic matter generates sufficient internal heat, resulting in ignition of surrounding brush.
- Weather Conditions: Prolonged drought greatly increases the risk of natural ignition by supplying ample dry fuel, exacerbating fire spread and intensity.
These natural phenomena, while constituting a smaller percentage of brush fires compared to human causes, can result in extensive ecosystem disruption.
Proactive measures and awareness can mitigate risks associated with these natural ignition sources.
Human Negligence and Brush Fire Incidents
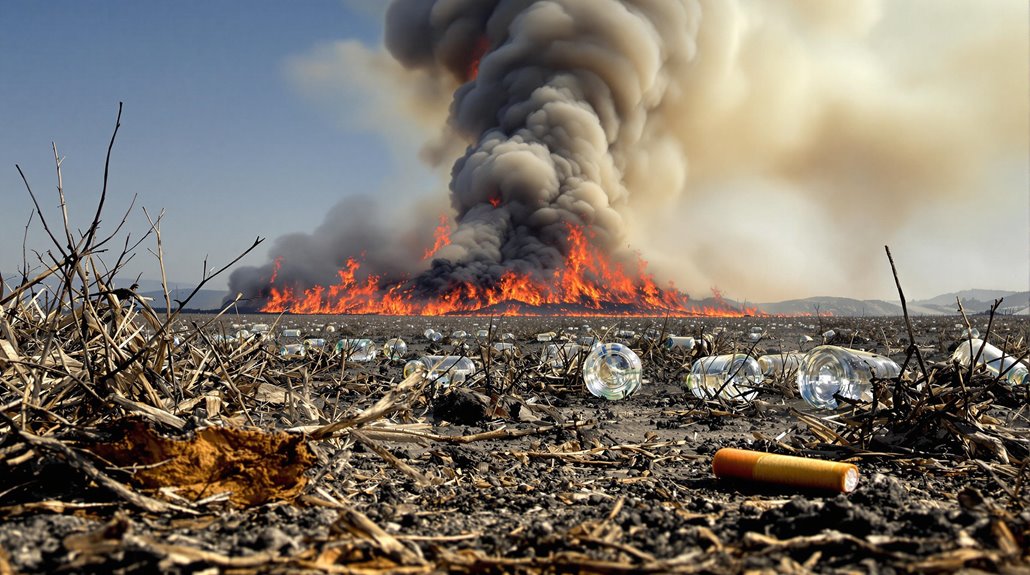

Human negligence considerably contributes to brush fire incidents, with improper debris burning and careless campfire practices being primary ignition sources.
Equipment spark hazards, stemming from engine malfunctions and faulty power lines, further exacerbate the risk of fire outbreaks.
Implementing stringent safety measures and public awareness campaigns is essential to mitigate these preventable causes and protect natural landscapes.
Careless Campfire Practices
Negligent campfire practices contribute substantially to the outbreak of brush fires, accounting for approximately 5% of wildfires across the United States.
Careless campfire practices often involve unattended campfires, which increase fire risks, especially in areas with dry vegetation. To mitigate these risks, campfires must be properly monitored and extinguished.
Following technical guidelines can help in safely managing campfire activities:
- Use designated fire rings and clear at least 10 feet of surrounding vegetation.
- Monitor campfires constantly, especially during windy conditions, to prevent embers from igniting dry vegetation.
- Extinguish campfires by thoroughly dousing them with water, stirring the ashes, and ensuring no residual heat remains.
- Refrain from leaving campfires unattended to prevent accidental escalation into brush fires.
Adherence to these safety practices is essential in preventing wildfires.
The fire triangle components of heat, fuel, and oxygen must all be eliminated when extinguishing a campfire to prevent reignition.
Improper Debris Burning
Improper debris burning, a significant contributor to brush fires, accounts for 29% of human-caused wildfires in the United States.
Outdoor burning of yard waste, especially without permits, poses substantial fire risks. A burn pile can rapidly escalate into a brush fire under hot, dry, or windy conditions.
Safety measures include maintaining a clear area three times the burn pile's height and at least 10 feet around it. Continuous monitoring post-burn is essential to guarantee all sparks and embers are fully extinguished, preventing reignition.
In the wildland-urban interface, where human habitation meets undeveloped land, consulting local fire departments is critical. They provide guidance on burn regulations, reducing the
Similar to home fire safety, having a designated meeting spot away from the burn area ensures everyone can be quickly accounted for if the situation becomes dangerous.
Equipment Spark Hazards
Equipment spark hazards present a significant risk factor in the ignition of brush fires, particularly due to malfunctions in internal combustion engines and electrical infrastructure. Sparks from machinery can become ignition sources, especially under dry conditions.
Human negligence exacerbates these risks, with brush fires often traced back to neglected equipment maintenance. Notable incidents like the Zaca Fire (2007) and Carr Fire (2018) highlight the dangers of improper upkeep.
Key considerations include:
- Equipment Malfunctions: Internal combustion engines and faulty power lines can emit sparks.
- Spark Arrestors: While effective, these devices can fail, particularly during extreme fire conditions.
- Proper Maintenance: Essential to prevent accidental ignition sources.
- Human Negligence: Ignoring malfunctioning equipment and safety protocols increases brush fire risks.
Preventative Measures to Minimize Risk

To effectively minimize the risk of wildfires, adherence to established safety protocols is essential. Wildfire risk, exacerbated by burning yard debris, necessitates understanding the fire triangle—heat source, fuel, and oxygen. Implementing wildfire safety preparation tips, such as clear communication with neighbors and creating defensible space around properties, can significantly reduce the likelihood of fires spreading. Additionally, communities should engage in regular fire drills and educational sessions to ensure everyone is aware of the risks and knows how to respond in the event of a wildfire. By fostering a culture of prevention and preparedness, we can collectively work towards safeguarding our environment and communities from devastating wildfires.
Human-caused incidents, such as sparks from a metal or improper disposal of cigarettes, demand strict safety measures. Before burning yard debris, acquire permits and comply with local regulations concerning weather and site safety. Maintain a clear area approximately three times the pile's height, with a minimum 10-foot buffer of non-flammable materials, mitigating the heat source's impact on drier vegetation.
Utilizing spark arrestors on equipment is vital to prevent accidental ignition from engine sparks. Regularly maintain equipment to forestall malfunction.
Cigarettes should be extinguished in soil, not on flammable surfaces, and never discarded from vehicles. Children must be supervised around fire-starting tools, with adult oversight imperative for all fire-related activities, including campfires and fireworks.
The Impact of Climate Change on Brush Fire Frequency

Climate change markedly influences the frequency and intensity of brush fires, primarily through the alteration of environmental conditions. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns contribute to prolonged dry spells, resulting in drier landscapes in the western United States. Such conditions increase the frequency and severity of brush fires by creating a highly flammable environment.
Key factors influenced by climate change include:
- Increased Average Temperatures: Higher temperatures lead to more rapid evaporation, reducing soil moisture and drying out vegetation, rendering it more flammable.
- Extended Fire Season: In regions like California, the fire season now starts earlier and lasts longer, expanding the window for potential fires.
- Prolonged Dry Spells: Climate-related droughts exacerbate the risk of brush fires by leaving vegetation dry and susceptible to ignition.
- Vegetation Growth and Flammability: Elevated carbon dioxide levels enhance plant growth, but subsequent drying increases flammability, raising the risk of fires.
Projections indicate significant future risks as climate change progresses.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Brush Fires Start Naturally?
Brush fires naturally ignite from lightning strikes, exacerbated by dry weather and specific vegetation types. Climate change intensifies drought conditions and alters seasonal factors, while wind patterns spread flames. Understanding these natural ignition sources is essential for safety.
Can a Brush Fire Start on Its Own?
A brush fire can start independently through spontaneous combustion of organic matter, lightning strikes, or chemical reactions. Extreme heat and dry conditions, coupled with specific weather patterns, greatly enhance the combustion process, making unintentional fires more probable.
What Causes a Brush Fire to Start?
When it rains, it pours issues for brush fires: dry conditions, lightning strikes, human negligence, and power lines contribute considerable. Discarded cigarettes, unattended campfires, agricultural practices, and arson activity exacerbate ignition risks, demanding increased vigilance and preventive measures.
What Creates a Brush Fire?
Brush fires arise from fire ignition sources like human activities and natural events. Environmental factors, seasonal conditions, drought influences, and vegetation types contribute. Human activities and lightning strikes generate sparks, igniting dry vegetation and facilitating rapid fire spread.
Final Thoughts
In examining the genesis of brush fires, it becomes clear that they symbolize nature's ever-precarious balance. Environmental conditions, human negligence, and natural phenomena act as tinder, sparking flames that mirror society's disregard for vigilance. Weather acts as an accelerant, driving the blaze forward, akin to the relentless march of time. To safeguard against this fiery dance, strategic prevention and awareness are essential. As climate change fans these flames, a collective responsibility to mitigate risk becomes vital for future resilience.
For homeowners facing property damage from brush fires or related incidents covered by their homeowners insurance policy, insurance industry professionals and legal experts strongly advise consulting a qualified state-licensed public adjuster. These professionals work exclusively for policyholders, not insurance companies, serving as dedicated advocates throughout the claims process. Public adjusters are state-licensed experts who help navigate complex insurance policies, identify hidden damages often unknown to policyholders, thoroughly document losses, and negotiate with insurance companies to ensure fair settlements while protecting policyholder rights.
By hiring a public adjuster, policyholders can maximize their claim payouts, expedite the claims process, and reduce the stress of dealing with insurance companies, allowing them to focus on recovery. Those seeking guidance with property damage or loss claims are encouraged to request a no-obligation free consultation with a Public Claims Adjusters Network (PCAN) member public adjuster through our contact page.