Home foundations come in various types, each suited to specific climates and soil conditions. Slab-on-grade foundations are ideal for warm climates, while full basement foundations are necessary in cold climates to prevent frost heave damage. Crawlspace foundations are suitable for areas with high water tables or unstable soils. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type, as well as structural elements and design considerations, is essential for selecting the most suitable foundation, and further exploration can reveal the intricacies of foundation choice and maintenance.
Key Takeaways
- Home foundations come in various types, including slab-on-grade, full basement, crawlspace, and specialized foundations like pile foundations.
- Foundation choice depends on factors such as climate, soil conditions, water tables, and region-specific requirements.
- Slab-on-grade foundations are suitable for warm climates, while full basement foundations are necessary in cold climates to prevent frost heave damage.
- Crawlspace foundations offer versatility and easier access but require regular maintenance to prevent moisture issues and structural damage.
- A well-designed foundation ensures structural integrity, durability, and stability, and is essential for the overall safety and longevity of a building.
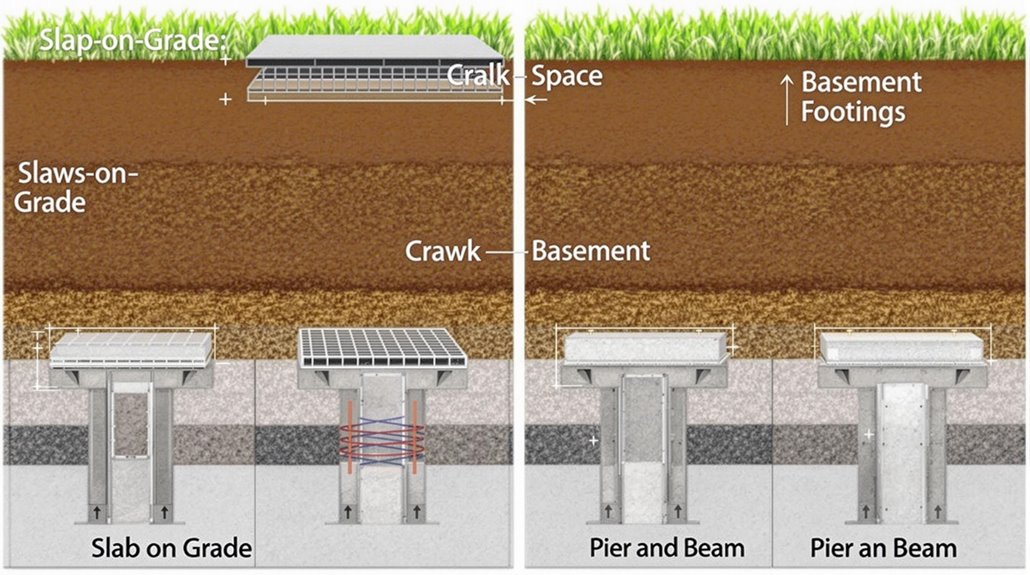
Types of Home Foundations and Their Geographic Suitability
When it comes to constructing a home, the type of foundation used is largely dependent on the geographic location and climate of the area. Different regions require specific foundation types to guarantee foundation stability and durability.
In warm climates, slab-on-grade foundations are often used due to their economical and fast construction benefits. In colder climates, full basement foundations are necessary to prevent damage from frost heave and guarantee structural stability.
Crawlspace foundations are commonly used in areas with high water tables or unstable soils, while specialized foundations such as pile foundations and ICF foundations are used in areas with unique soil conditions or high seismic activity.
The choice of foundation materials and type is essential in guaranteeing the foundation's stability and longevity. A foundation's primary purpose is to transfer load to the ground, which is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of the building.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Foundation Types
Because the type of foundation used in constructing a home plays a crucial role in its stability and longevity, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of different foundation types is essential in making informed decisions.
Foundation costs and durability are key considerations in this decision-making process.
Concrete slab foundations are cost-effective and strong, but prone to cracking and lack extra storage space.
Crawlspace foundations offer versatility and easier access to structural components, but require proper maintenance to prevent moisture issues.
Basement foundations provide additional living space, but are more expensive to build and require additional waterproofing measures. A geotechnical engineer should supervise soil compaction to prevent settlement issues, especially for homes built on problematic soil types.
Ultimately, weighing the pros and cons of each foundation type allows homeowners to choose the most suitable option for their specific needs and budget.
Structural Elements and Design Considerations for Foundations
Home foundation design is heavily influenced by the type of foundation chosen, with its structural elements playing a significant role in the overall stability and longevity of the home.
Key components such as footings, foundation walls, piers, columns, and concrete slabs work together to distribute loads and resist lateral pressure. The selection of foundation materials, including rebar for added strength and stability, is critical in achieving a durable foundation.
Load distribution is a critical design consideration, as it directly impacts the foundation's ability to support the structure above. Proper design requires consideration of soil conditions, settlement, and erosion, as well as adherence to design principles that guarantee safe and efficient load distribution over the foundation bed. Ensuring high stability in collapsible soils is crucial for structural integrity.
Effective foundation design often requires the expertise of a qualified structural engineer.
Climate and Site Conditions That Influence Foundation Choice
Climate and site conditions are vital factors that greatly influence the selection and design of a foundation.
Climate variability, in particular, plays a significant role in determining the type of foundation suitable for a specific region. For instance, areas with high water tables or prone to heavy rainfall require specialized foundation designs, such as waterproofing measures or pile foundations, to mitigate hydrostatic pressure and water accumulation.
Soil analysis is also important in foundation selection, as climate impacts soil moisture levels and freeze-thaw cycles, affecting foundation stability. Expansive clay soils, for example, require specialized solutions like moisture barriers or chemical stabilization to guarantee foundation longevity.
A thorough understanding of climate and site conditions is essential for designing a durable and resilient foundation.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations for Various Foundation Types
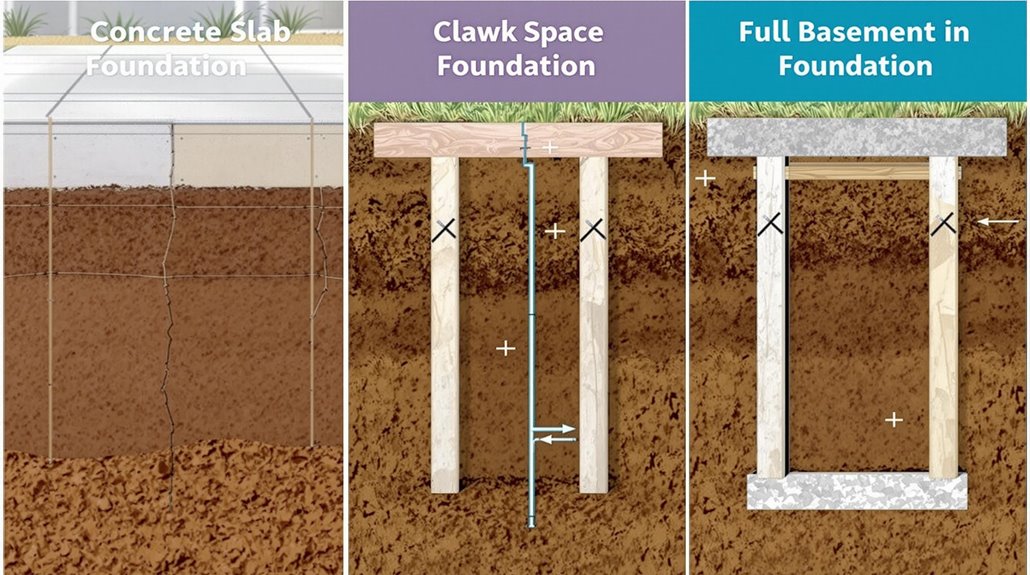
A well-designed foundation, informed by thorough climate and site analyses, is only the first step in ensuring the stability and longevity of a structure.
Regular foundation inspections are vital to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. Moisture management is also essential to prevent structural issues and damage.
Crack repair, terrain stability, and professional assessments are additional maintenance considerations. Various repair methods, such as slab jacking, piering, and concrete resurfacing, are used to address foundation issues.
The cost of repairs varies widely based on the foundation type, extent of damage, and necessary repairs, ranging from $500 to $3,000 or more for extensive repairs.
Effective maintenance and prompt repairs are imperative to extending the lifespan of a foundation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Change My Home's Foundation Type After It's Been Built?
Approximately 15% of homes require major foundation repairs. Changing a home’s foundation type after construction is possible, involving complex foundation modifications that require careful planning to maintain structural integrity and prevent further damage. Homeowners considering such modifications should first identify common foundation problems in homes, which can include cracks in walls, uneven flooring, and doors that stick. Addressing these issues early on can help prevent the need for extensive repairs down the line. It’s also advisable to consult with foundation specialists who can provide tailored solutions to ensure the long-term stability and safety of the home.
What Is the Average Lifespan of a Residential Home Foundation?
The average lifespan of a residential home foundation is 80-100 years, influenced by lifespan factors such as weather, construction quality, and environmental conditions. Regular foundation maintenance, including inspections and repairs, can greatly extend its lifespan.
How Do Local Building Codes Impact My Foundation Choices?
Maneuvering the complex web of local building codes, a homeowner's foundation choices are governed by stringent foundation regulations, necessitating building permits that guarantee compliance, safeguarding the structure's integrity and longevity amidst environmental and climatic challenges.
Can I Build a Home Foundation on Uneven or Sloping Land?
Building a home foundation on uneven or sloping land is feasible with careful planning and specialized design considerations, including slope considerations and potential foundation adjustments to address differential settlement and guarantee structural integrity.
Are There Any Foundation Types That Are More Resistant to Pests and Rodents?
Foundations constructed with pest-resistant materials, such as concrete, stone, and insulated concrete forms, provide effective rodent prevention. Incorporating design elements like termite shields, graded particles, and sealed joints further enhances pest resistance.








