Foundation gaps are caused by soil settling, moisture variations, inadequate drainage, and temperature changes. Common types include vertical, horizontal, and diagonal gaps, each indicating different issues such as settling or soil pressure. Repairs can range from $250 for minor cracks to over $36,500 for severe problems, employing techniques like epoxy injections or underpinning. Understanding repair cost factors and preventive strategies is essential for effective maintenance, offering further insights into safeguarding property integrity.
Key Takeaways
- Foundation gaps can be vertical, horizontal, or diagonal, each indicating different structural issues like settling or soil movement.
- Causes of foundation gaps include moisture fluctuations, soil expansion, tree roots, inadequate drainage, and extreme temperature changes.
- Repair costs vary widely: minor crack repairs range from $250 to $800, while extensive interventions can exceed $15,000.
- Common repair methods include epoxy injections, piering, slabjacking, fortress stabilization, and waterproofing, with costs depending on damage severity and site conditions.
- Regular inspections and proper drainage management are key preventive measures to minimize foundation gaps and repair costs.
Understanding Foundation Gaps
Understanding foundation gaps necessitates an analytical examination of the underlying factors contributing to their formation. Foundation gaps often result from soil settlement, moisture fluctuations, and inadequate drainage.
These conditions lead to structural instability, manifesting as cracks in walls, uneven floors, and separations around doors and windows. Such indicators are common signs of potential structural issues that require immediate attention to prevent further deterioration.
Repair costs for addressing foundation gaps vary considerably, depending on the severity and repair method chosen. Minor crack repairs might average around $300, while extensive structural interventions, such as piering or underpinning, could escalate to $15,000 or more.
Techniques like epoxy injections are suitable for minor cracks, while severe issues may necessitate more complex solutions. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the foundation can mitigate the risk of gap formation, thereby reducing potential repair costs and safeguarding structural integrity over time.
Common Types Of Foundation Gaps
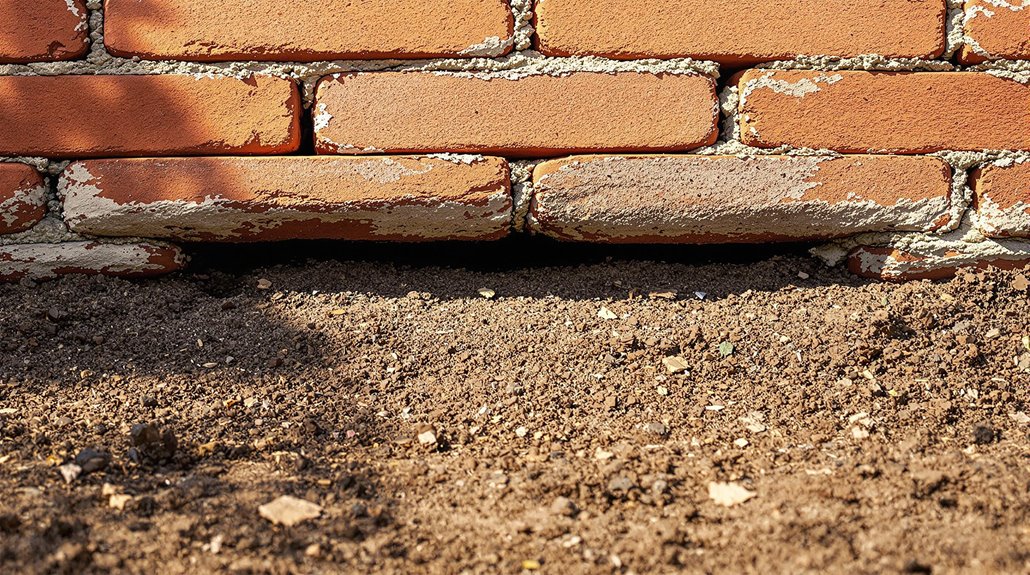

Foundation gaps manifest in various forms, each indicating specific underlying structural or environmental issues.
Vertical gaps frequently appear at corners of doors and windows, suggesting foundation settling or shifting, which can escalate repair costs if not addressed promptly.
Horizontal gaps, often found in basement walls, imply significant lateral pressure or bowing due to soil conditions, necessitating interventions like wall anchors or braces.
Diagonal gaps, typically emerging in walls, are indicative of uneven settling or soil movement and require thorough assessment to prevent further damage.
Foundation cracks, prevalent in concrete slabs or block foundations, arise from natural settling or moisture variation.
While minor cracks may demand minimal repair costs, larger ones could signify critical structural problems requiring extensive solutions.
Additionally, gaps around the foundation can lead to water accumulation and erosion, underscoring the need for effective drainage systems.
Understanding these gap types is essential in diagnosing the causes of foundation issues and determining appropriate remedial actions.
Causes Of Foundation Gaps
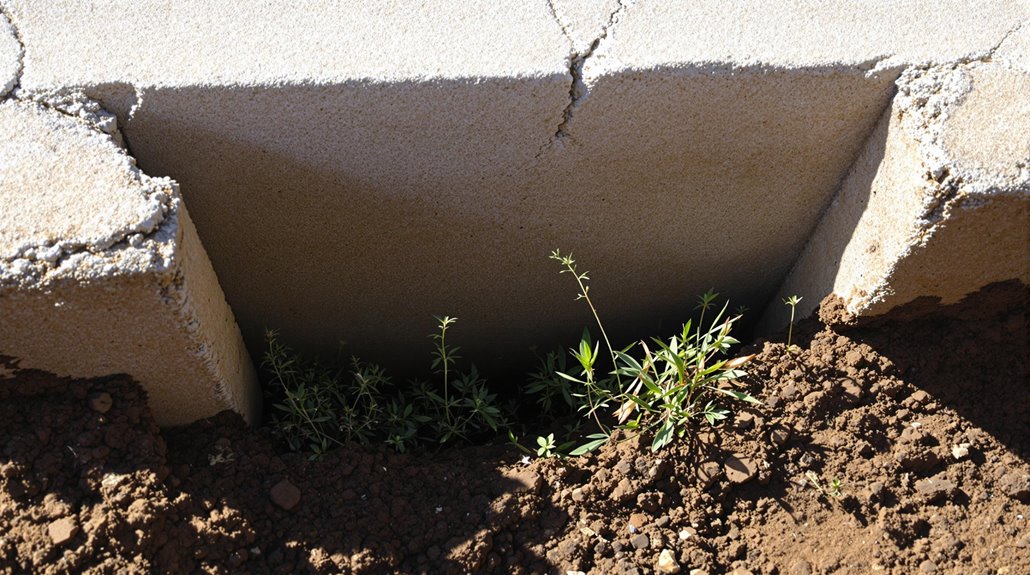

Amidst various contributing factors, excessive moisture in the soil emerges as a primary cause of foundation gaps, as it leads to expansion and contraction that destabilizes structural integrity.
The cyclical nature of soil swelling and shrinkage under varying moisture conditions exacerbates foundation instability. Tree roots, when growing in close proximity, can exert significant pressure, displacing soil and further aggravating foundation gaps.
Inadequate drainage systems compound these issues by allowing water to accumulate near the foundation, eroding the soil and creating voids. This erosion undermines the foundation’s support, contributing to the development of gaps.
Additionally, extreme temperature fluctuations can induce soil movement, with thermal expansion and contraction impacting the foundation’s alignment.
Improper construction practices, such as insufficient footings, further predispose structures to foundational instability. These practices fail to accommodate soil dynamics, ultimately leading to the formation of foundation gaps.
Understanding these causes is essential for implementing effective preventative measures.
Symptoms Of Foundation Gaps
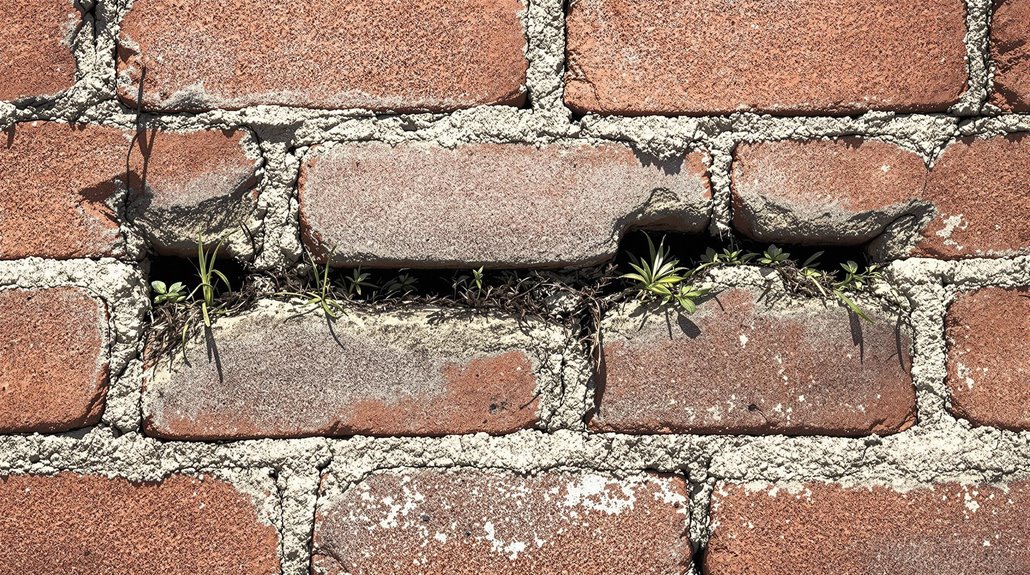

Recognizing the symptoms of foundation gaps is imperative for timely intervention and mitigation of structural issues.
These symptoms often manifest in various forms, indicating the presence of underlying problems that may require immediate attention. Observations include:
- Visible Cracks: Cracks in walls, floors, or ceilings often serve as initial indicators of shifting or settling foundations. Such cracks suggest potential gaps that demand inspection and potential repair.
- Sticking or Misaligned Doors and Windows: When doors and windows fail to open or close smoothly, it indicates misalignment, a symptom of foundation movement creating gaps in the structure.
- Uneven or Sloping Floors: Floors that appear uneven or sloped reveal discrepancies between floor levels and walls, suggesting significant foundation gaps.
Additional symptoms can include gaps around window frames or doors and water pooling around the foundation.
These highlight the urgency of addressing foundation gaps to prevent further structural degradation and guarantee energy efficiency.
Assessing Foundation Damage

Evaluating foundation damage necessitates a systematic approach to identify indicators such as wall cracks, sloping floors, and misaligned doors or windows, which signal potential destabilization of the foundation. Recognizing these signs of foundation problems is critical in determining foundation damage, as each symptom may point to compromised structural integrity. The extent of the damage can vary greatly, with repair costs influenced by foundation types, severity, and site conditions.
Different foundation types, such as slab, pier and beam, and basement foundations, present unique challenges in evaluation and repair. Accessibility markedly impacts repair complexity and costs, as difficult-to-reach areas may require specialized equipment or techniques.
| Foundation Type | Typical Issues | Repair Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Slab Foundation | Cracks, moisture | $500 – $10,000 |
| Pier and Beam | Sagging, shifting | $1,000 – $15,000 |
| Basement | Wall bowing, leaks | $2,000 – $36,500 |
Prompt evaluation and repair avert escalating damages and expenses.
Evaluating Repair Needs
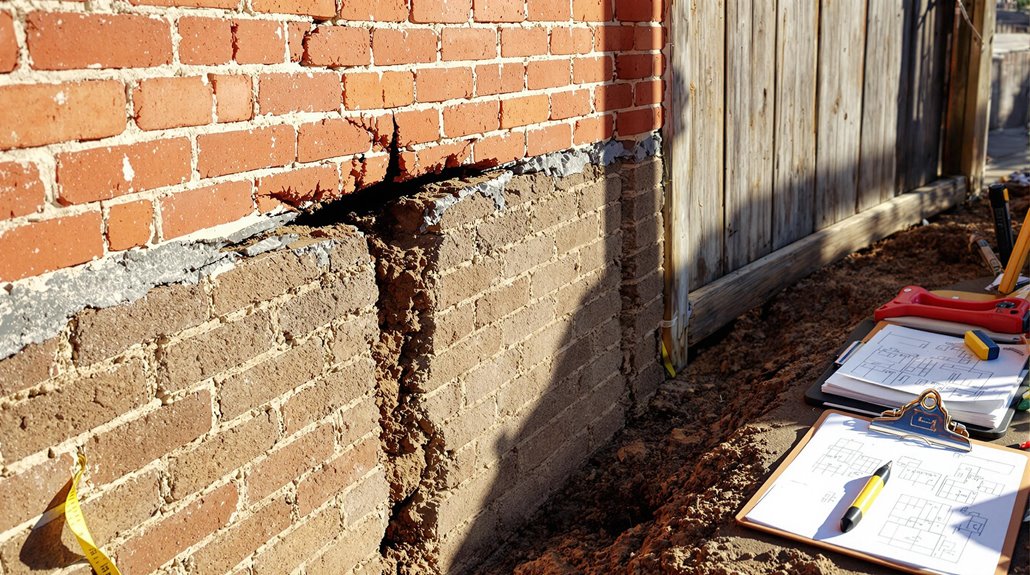

Determining the appropriate repair needs for foundation gaps requires an extensive analysis of the damage’s severity and causes.
Professional assessments are vital for accurately evaluating the extent of the damage, with inspection costs ranging from $75 to $500. The type of foundation—be it slab, pier and beam, or basement—significantly influences both the repair methods and repair costs involved in foundation repair projects.
- Minor Gaps: Repairs may range from $250 to $800, addressing issues like small cracks or slight misalignments.
- Severe Structural Issues: Repair costs can escalate to $10,000 or more, requiring thorough solutions like underpinning.
- Repair Methods: Techniques such as epoxy injections or underpinning vary in cost. Underpinning, for example, ranges from $6,000 to $36,500, based on the severity.
Early detection and timely professional assessments are essential, potentially saving homeowners from substantial repair costs by addressing foundation gaps before they exacerbate.
Common Foundation Repair Techniques

A thorough understanding of common foundation repair techniques is vital for addressing structural issues effectively. Among these techniques, epoxy injection is frequently used to seal cracks, with foundation repair costs typically ranging from $300 to $1,000.
For stabilizing a foundation experiencing settlement, piering or underpinning methods are employed, costing between $1,000 and $3,000 per pier.
Slabjacking, another prevalent technique, involves raising sunken concrete slabs by injecting material underneath, with expenses spanning from $1,000 to $25,000, contingent on the project’s extent.
Fortress stabilization, using carbon fiber and Kevlar strips, is particularly effective for reinforcing bowing walls, averaging around $13,000.
Additionally, waterproofing solutions play an important role in preventing moisture-related issues and range from $2,000 to $10,000.
The selection of repair techniques is influenced by the foundation type, damage severity, and site conditions, all of which greatly impact the complexity and foundation repair costs.
Cost Factors In Foundation Repairs
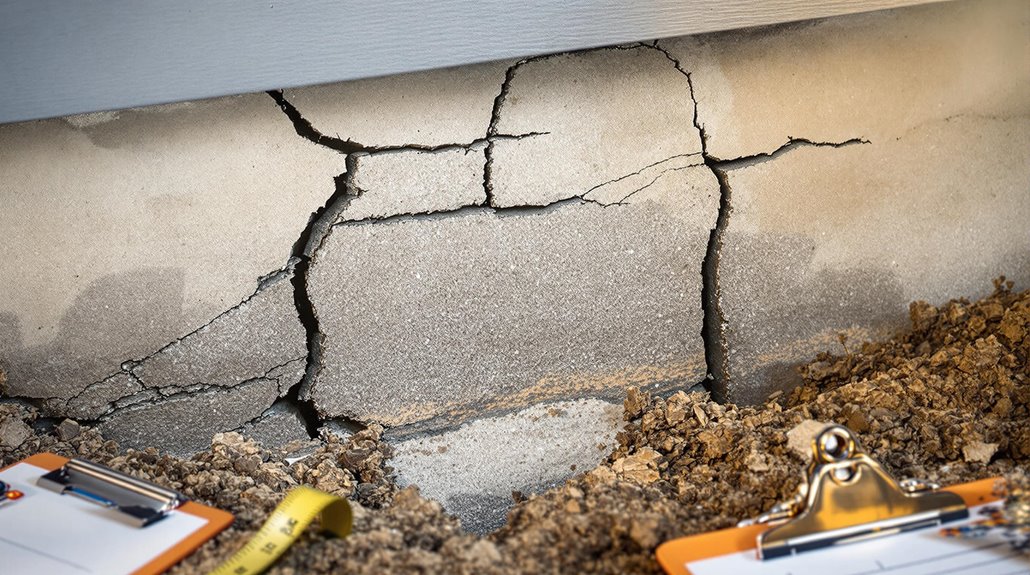

Understanding the costs associated with foundation repair requires a thorough analysis of various influencing factors. Each element plays a critical role in determining repair costs, necessitating a precise evaluation.
- Foundation Type: Repair costs are heavily contingent upon the type of foundation. Concrete slab foundations generally incur lower expenses, while pier and beam or basement foundations can escalate costs due to their complex nature.
- Local Labor: Geographic location greatly impacts costs, with local labor rates and material prices varying. Urban areas typically experience higher expenses, affecting the overall repair budget.
- Severity of Damage: The extent of structural damage is a pivotal determinant. Minor issues might be resolved with costs as low as $250, whereas severe damage requiring extensive solutions can reach upwards of $36,500.
These factors underscore the necessity for a thorough assessment to accurately estimate repair costs, enabling informed decision-making and effective financial planning in addressing foundation issues.
Comparing Repair Costs

When evaluating foundation repair costs, it is essential to contemplate the specific methodologies employed, as expenses can vary considerably based on the approach selected.
Repair costs for foundation damage are heavily influenced by the types of repair needed. For instance, addressing minor cracks might incur costs ranging from $250 to $800 per crack, depending on severity. In contrast, more extensive damage requiring underpinning or wall stabilization can escalate costs significantly, often ranging from $1,000 to $3,000 or more. The choice of foundation crack repair methods also plays a crucial role in determining the overall expense, as some techniques may require advanced materials or specialized labor. Homeowners should carefully consider these options and consult with professionals to ensure a lasting solution to their foundation issues.
Conversely, foundation stabilization strategies, such as underpinning, exhibit a broader spectrum in repair costs, with the average cost of foundation work ranging from $6,000 to $36,500.
Piering, a prevalent method for significant foundation damage, typically commands $1,000 to $3,000 per pier, with multiple piers often necessary.
Additionally, waterproofing solutions, vital for preventing moisture-related issues, generally range from $2,000 to $10,000.
Understanding these variances in repair costs is fundamental for accurately anticipating financial obligations, enabling homeowners to make informed decisions based on the extent and nature of the foundation damage encountered.
Preventive Measures For Foundation Health
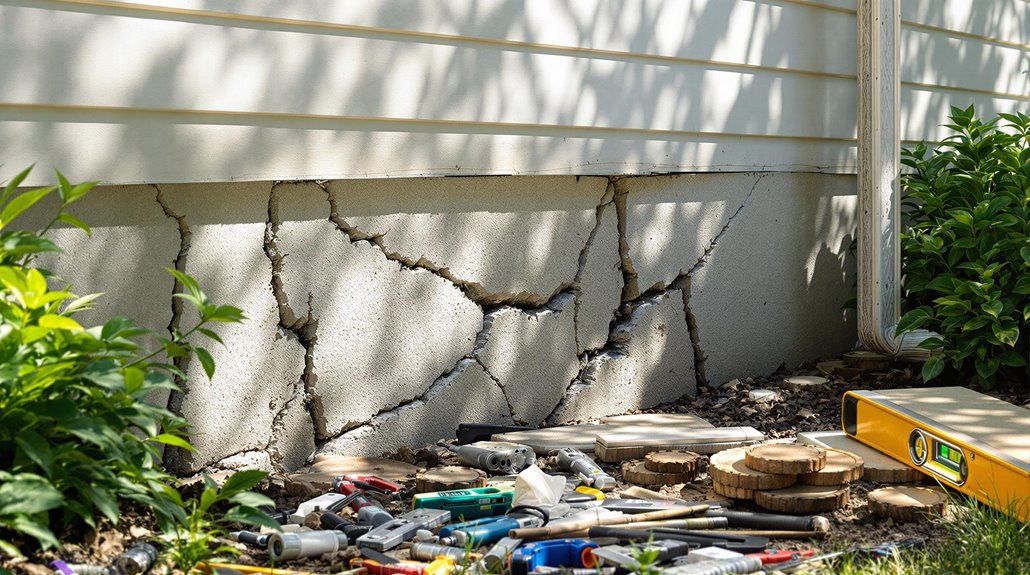

Analyzing foundation repair costs reveals the financial impact of addressing structural damage, emphasizing the importance of proactive measures to avert potential expenses.
Preventive strategies can greatly mitigate risks associated with foundation gaps. Key recommendations include:
- Drainage Management: Guarantee proper drainage around the property by directing water at least 5-10 feet away from the foundation, thereby preventing water damage and soil erosion.
- Soil Moisture Regulation: Maintain consistent soil moisture levels to reduce soil expansion and contraction, consequently minimizing the likelihood of developing cracks in your walls.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections by qualified professionals to detect early signs of structural issues and address them before they necessitate costly repairs.
Additionally, attention to surrounding vegetation is vital.
Avoid planting trees within 10-20 feet of the foundation to prevent root systems from compromising soil stability.
Promptly repair any visible cracks to prevent escalation.
These measures collectively enhance foundation health and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Type of Foundation Repair Is Most Expensive?
Underpinning emerges as the most costly foundation repair, ranging from $6,000 to $36,500. This technique addresses severe structural issues by reinforcing foundation stability, necessitating significant labor and materials, hence explaining its higher expense compared to other methods.
What Is the Most Foundation Repair Can Cost?
Foundational failures can financially burden homeowners, with costs potentially surpassing $50,000. Complete replacements represent the pinnacle of price, propelled by pervasive problems. Precision in early detection can prevent pervasive expenses, emphasizing efficiency in evaluation and execution of repairs.
How Do You Know if Your Foundation Needs Repair?
Indicators of necessary foundation repair include wall or floor cracks, misaligned doors or windows, and uneven floors. These symptoms suggest structural instability requiring professional assessment to determine the extent of damage and appropriate remediation strategies.
Do Foundation Repairs Devalue a Home?
Like a phoenix from ashes, foundation repairs, when executed meticulously, can enhance a home’s market value. These repairs, fortified by warranties, often dispel buyer skepticism, transforming perceived liabilities into assets, thereby stabilizing or increasing property value.