Tree roots can greatly impact house foundations by exerting pressure that leads to cracks and structural instability. Roots, particularly from trees like oaks and silver maples, infiltrate foundation cracks and plumbing systems, absorbing moisture and causing soil depletion. This results in uneven settling and potential damage. Identifying root-induced issues involves evaluating foundation cracks and plumbing problems. Root barriers and maintaining appropriate distance are essential prevention strategies. Professional insights provide thorough solutions and strategies for long-term tree management near foundations.
Key Takeaways
- Tree roots can apply pressure against foundations, leading to cracks and structural damage.
- Invasive root systems, like those of oaks and silver maples, infiltrate foundation cracks and plumbing lines.
- Absorption of moisture by roots causes dry soil, leading to foundation sinking and movement.
- Regular inspections and root barriers help prevent root-induced foundation problems.
- Root pruning or removal may be necessary for trees with aggressive root systems.
Understanding How Tree Roots Affect Foundations
Tree roots pose a significant threat to house foundations due to their natural growth patterns and quest for essential resources. As roots extend horizontally, they can apply pressure against foundations, leading to cracks and potential structural damage.
Invasive root systems, particularly from species like oaks and silver maples, infiltrate pre-existing foundation cracks or plumbing lines, exacerbating deterioration. The absorption of moisture by tree roots results in dry soil, causing foundation sinking and movement. This soil depletion can intensify foundation damage over time.
Implementing root barriers and maintaining a safe distance between trees and structures are effective strategies to prevent foundation damage. By controlling moisture levels and managing root encroachment, property owners can mitigate risks and preserve structural integrity.
Common Trees That Cause Foundation Damage

In the domain of residential structural integrity, the impact of specific tree species on house foundations is a subject of technical concern and analysis.
Certain common trees, such as Liquid Amber, Ficus, eucalyptus, and Sweetgum, exhibit invasive root systems. These root systems aggressively penetrate and destabilize nearby foundations, exacerbating structural issues.
Oaks, responsible for approximately 11% of reported foundation problems, possess shallow roots that deplete water and nutrients from moist soil, further compromising house foundations.
Poplars, reaching up to 100 feet, have lateral-spreading shallow roots that threaten foundations when planted in proximity.
Ash tree roots can extend 30 feet, causing shifts in stability.
Additionally, Norway maples, silver maples, honey locusts, and sycamores contribute to foundation damage through their invasive root systems.
Identifying Signs of Root-Induced Foundation Issues
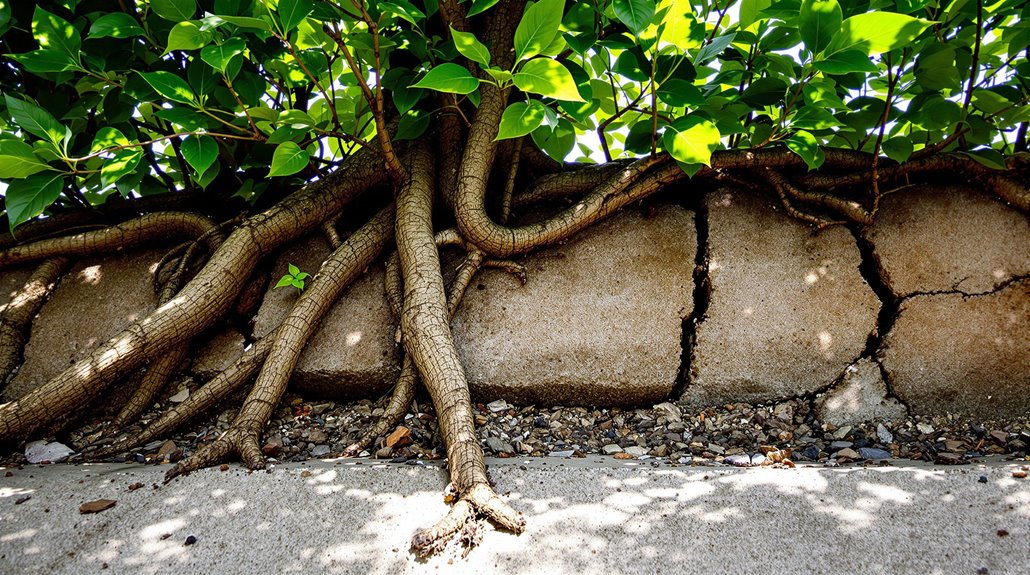

How can homeowners accurately identify signs of root-induced foundation issues? Key indicators include cracks in foundation walls and floors, which may arise from tree roots applying pressure or altering the soil composition.
A home leaning towards surrounding trees might signify uneven foundation settling due to moisture extraction by roots.
Buckling or heaving concrete surfaces serve as evidence of compromised structural integrity, often linked to active root systems.
Plumbing issues, such as clogged drains, can further suggest root infiltration, as roots penetrate sewer lines through existing cracks, compounding damage.
Regular monitoring, especially near trees with invasive root systems, is essential for early detection.
Observing these signs allows homeowners to address potential root-induced damage before it escalates, safeguarding the foundation's integrity.
Preventative Measures to Protect Foundations From Tree Roots

In addressing the protection of house foundations from tree roots, strategic planning begins with maintaining ideal tree planting distances, specifically 10 to 20 feet for smaller species and up to 50 feet for larger ones, to mitigate root encroachment.
Implementing effective root barrier systems serves as a critical intervention to channel root growth away from foundation structures, thereby preserving their integrity.
Additionally, selecting non-invasive tree species characterized by slower growth rates and shallow root systems can greatly reduce the potential for root-related foundation damage.
Effective Root Barrier Strategies
To effectively prevent tree roots from compromising house foundations, implementing root barrier strategies is vital.
Root barriers, composed of thick, solid materials, serve to redirect tree roots, thereby mitigating foundation damage. Proper placement is essential; barriers should be installed at least two feet deep to reach the root zone, guaranteeing lateral growth towards foundations is prevented.
Regular inspections are imperative, as invasive roots may exploit any weaknesses in the barriers. These barriers are often best complemented by strategic tree planting, maintaining a distance of 10 to 20 feet from the foundation.
Utilizing professional services can guarantee that root barriers are installed correctly, maximizing their effectiveness. This multifaceted approach aids in preventing future problems associated with invasive root systems.
Ideal Tree Planting Distances
While root barriers serve as a formidable defense against invasive tree roots, their effectiveness is greatly augmented by adopting strategic tree planting practices. Correct planting distances are critical in preventing damage to house foundations. Fast-growing trees, such as poplars, require larger separations of 30 to 50 feet due to aggressive root systems. Shallow-rooted trees, like oaks, contribute to foundation problems if not properly spaced.
| Tree Type | Recommended Distance |
|---|---|
| Small Trees | 10 to 20 feet |
| Fast-Growing Trees | 30 to 50 feet |
| Shallow-Rooted Trees | 30 to 50 feet |
Positioning trees further away guarantees roots do not exploit moist soil near foundations, minimizing potential damage. Selecting non-invasive species and employing root barriers can mitigate risks, safeguarding structural integrity.
Non-Invasive Tree Selection
Given the potential risks tree roots pose to house foundations, selecting non-invasive tree species emerges as an essential preventative measure.
Species like dogwoods and redbuds, characterized by shallower, less aggressive root systems, considerably reduce foundation damage risk. Ensuring a planting distance of at least 10 to 20 feet, or greater for larger trees, is imperative in safeguarding structural integrity.
Root barriers serve an important role by directing roots deeper, away from foundation walls. Incorporating slow-growing trees such as hawthorn or serviceberry, which demand minimal water, further minimizes encroachment risks.
Proper placement, guided by arborists, is essential to prevent future complications. Expert consultation aids in selecting appropriate varieties, ensuring a harmonious balance between landscape aesthetics and structural safety.
Effective Strategies for Repairing Foundation Damage

Detecting and addressing foundation damage early is essential to preventing extensive structural issues caused by invasive tree roots.
Regular inspections for cracks or shifting are important, allowing for immediate damage assessment and intervention. Consulting a foundation repair professional can identify the extent of the damage and propose solutions like root pruning or removal.
Implementing root barriers can effectively redirect tree roots away from the foundation, minimizing future risks. In cases where trees with aggressive root systems are too close to a home, strategic trimming or complete removal may be necessary.
Additionally, repairing any plumbing leaks without delay is critical, as moisture can attract tree roots, worsening foundation damage.
Excavation may also be required to access and repair affected areas efficiently.
The Role of Professional Assessment and Intervention
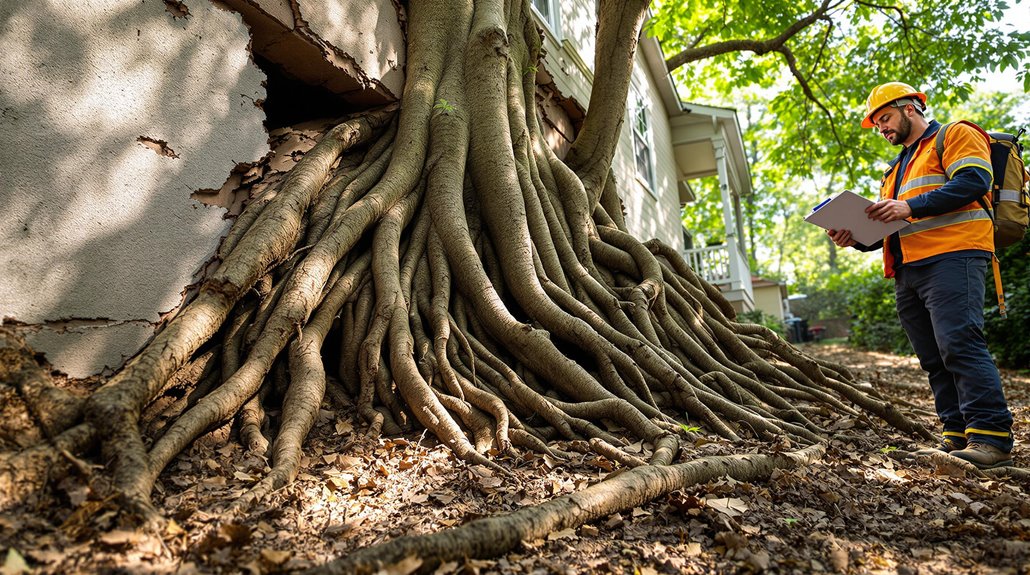

Addressing foundation damage effectively requires more than immediate repair actions; it necessitates a thorough evaluation of potential risks posed by tree roots.
Professional assessments by certified arborists enable identification of tree species and root behaviors impacting foundation integrity. This informed approach guides foundation repair strategies, targeting structural damage with solutions such as root barriers.
Before commencing landscaping projects, consulting experts guarantees tree planting occurs at safe distances, mitigating future risks. Regular assessments monitor tree growth and root activity, allowing early detection and intervention to prevent severe damage.
Engaging local experts, knowledgeable in regional soil and tree conditions, provides valuable insights for maintaining foundation integrity. Such strategic interventions guarantee the longevity and stability of residential structures against the encroachment of tree roots.
Long-Term Management of Trees Near Foundations
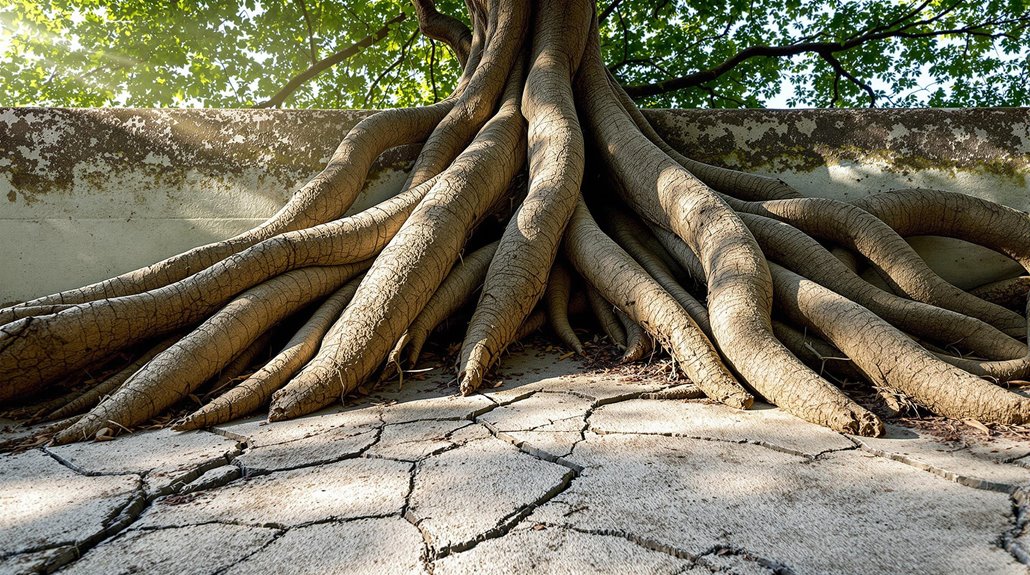

Long-term management of trees near foundations necessitates strategic measures such as root barrier installation and regular tree assessments to mitigate structural risks.
Root barriers are engineered solutions designed to guide root growth away from foundations, thereby reducing the likelihood of root-induced damage.
Concurrently, periodic assessments by certified arborists guarantee early identification of potential issues and facilitate the implementation of corrective actions, optimizing both tree health and structural integrity.
Root Barrier Installation
Installing root barriers presents a strategic solution for managing potential conflicts between tree roots and house foundations, particularly in urban and suburban environments.
These barriers, composed of durable materials like solid plastic or metal, are installed vertically in the soil to redirect root systems, thereby preventing foundation damage.
To effectively block aggressive roots, such as those of oaks and silver maples, barriers should be installed at a minimum depth of 24 inches.
An arborist's expertise is advisable to guarantee ideal placement, considering specific tree types and local soil conditions.
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential, as roots may circumvent barriers over time.
Professional consultation aids in selecting appropriate materials and installing root barriers effectively to mitigate long-term risks.
Regular Tree Assessments
When managing trees near house foundations, regular tree assessments are essential for mitigating potential risks associated with invasive root systems.
Evaluating the proximity of trees, particularly species like oaks and poplars, is vital to prevent foundation damage. Tree roots cause damage by expanding horizontally until they encounter hard surfaces, then shifting downward.
Annual assessments help homeowners detect early signs, such as cracks caused by root pressure. Engaging a certified arborist during these evaluations provides expert insights into the root system's health and potential threats to homes.
Recommendations for preventive measures, including root barriers, can be made. Maintaining detailed records of tree assessments and any interventions guarantees effective long-term management, safeguarding both the structural integrity of foundations and the health of adjacent trees.
Final Thoughts
In the shadowy dance between nature and architecture, the threat of tree roots encroaching upon house foundations looms ominously. With each unnoticed crack and subtle shift, the structural integrity of homes hangs in precarious balance. As homeowners grapple with identifying and mitigating these subterranean forces, they stand at a crossroads where timely professional assessment and strategic interventions become paramount. Will foresight and preventative action prevail, or will the silent undercurrents of nature claim their next victim?
For homeowners experiencing foundation damage potentially caused by tree roots, consulting with a state-licensed public adjuster is essential before filing an insurance claim. These licensed professionals work exclusively for policyholders, not insurance companies, and specialize in identifying covered damages that homeowners might overlook. Public adjusters thoroughly assess foundation damage, document all losses, and negotiate with insurance companies to ensure fair settlements that respect policyholders' legal rights. Their expertise in navigating complex insurance policies and claim procedures can significantly increase claim payouts while reducing stress during the claims process. Homeowners seeking expert guidance can request a free, no-obligation consultation with a Public Claims Adjusters Network (PCAN) member at PublicClaimsAdjusters.io/contact-us/ or by clicking "Free Consultation" at the top of this page.