Black mold, scientifically known as Stachybotrys chartarum, appears as dark green or black patches with a slimy or wet texture. It thrives in damp, cellulose-rich environments such as paper, wood, and drywall. Visible colonies can develop within 3-7 days after moisture damage. Black mold emits a strong, musty odor reminiscent of decay, even when not visible. To understand the signs of black mold infestation, its differences with mildew, and the associated health risks, further exploration is necessary.
Key Takeaways
- Black mold appears as dark green or black patches with a slimy or wet texture.
- It has a distinctive appearance with visible colonies that can develop within 3-7 days after moisture damage.
- Black mold thrives in damp, cellulose-rich environments such as paper, wood, and drywall.
- It can be identified by a strong, musty odor reminiscent of decay, even when not visible.
- Black mold can be distinguished from mildew by its darker color and deeper penetration into materials.
What Is Black Mold?
Because it is a microorganism that can have significant health implications, understanding the characteristics of black mold is essential.
Black mold, scientifically known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a dark green or black fungus that thrives in damp, cellulose-rich environments. It requires high levels of moisture to grow, which is why it is commonly found in areas with high humidity, such as basements, bathrooms, and around plumbing leaks.
Black mold growth poses serious health risks, particularly to individuals with allergies or weakened immune systems, due to the release of mycotoxins. While visible mold can be a clear indicator of black mold presence, it is not always immediately visible.
However, its strong, musty odor can make it detectable even when not visible. Understanding the characteristics of black mold can help individuals identify and address potential growth areas, mitigating health risks and preventing further growth.
High humidity and moisture-rich environments foster black mold growth.
Any visible black mold growth exceeding 10 square feet requires immediate professional remediation to ensure safety.
Identifying Black Mold
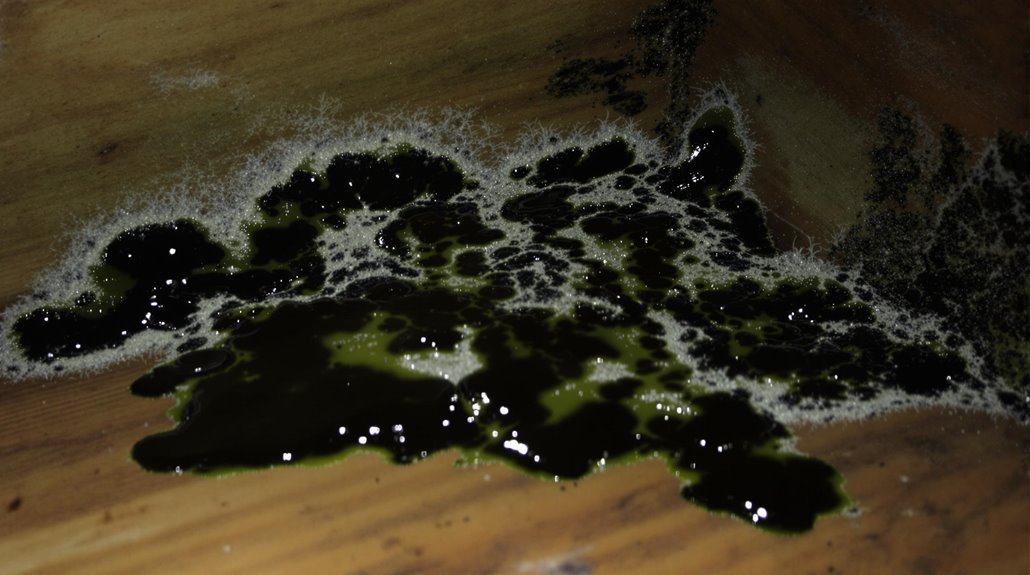

The identification of black mold is an essential step in mitigating its health risks and preventing further growth.
To identify black mold, one must know its distinctive appearance. Black mold, or *Stachybotrys chartarum*, typically appears as dark green or black patches with a slimy or wet texture. It often grows in clusters and may have fuzzy white edges, distinguishing it from other molds.
Black mold thrives on cellulose-rich materials like paper, wood, and drywall, making these surfaces common locations for infestation. It is usually found in damp areas of the home, such as basements, bathrooms, and around water leaks, where moisture levels are consistently high.
A musty odor reminiscent of decay often accompanies black mold growth. If you notice a musty smell in areas of your home prone to moisture, it may indicate black mold exposure.
Accurate identification is essential to prevent common health issues associated with black mold.
Visible colonies typically develop within 3-7 days after moisture damage occurs when conditions are optimal.
Signs of Black Mold Infestation
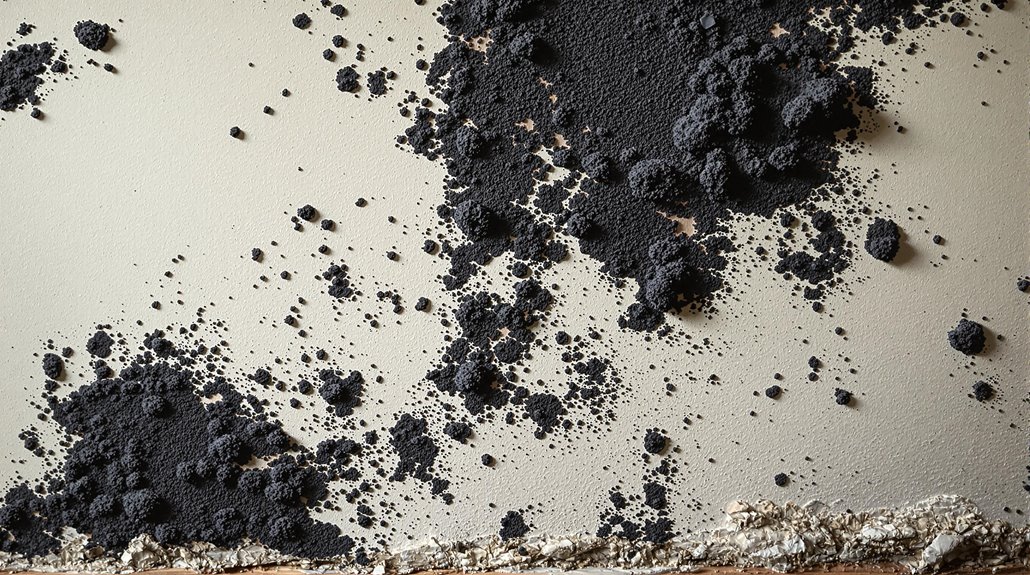

While black mold can be visible in the form of dark patches, its presence is not always apparent to the naked eye. A black mold infestation may be indicated by several signs, including the presence of moisture, a musty odor, and symptoms of exposure.
*Common signs of a black mold infestation include:*
- Visible water damage: Discoloration or warping of surfaces, indicating a water leak or flooding, which can lead to mold growth.
- Musty odor: A strong, unpleasant smell, often described as earthy or similar to rotting vegetables, frequently accompanies black mold infestations.
- Symptoms of exposure: Nasal congestion, coughing, and eye irritation can indicate a black mold presence even if it is not immediately visible.
Common inspection areas include under sinks, around toilets, in basements, and near windowsills.
Investigating these areas can help identify signs of mold infestation, allowing for prompt action to mitigate the issue.
Black mold typically thrives in environments with 70-90% moisture levels and temperatures between 60-80 degrees Fahrenheit.
Difference Between Black Mold and Mildew
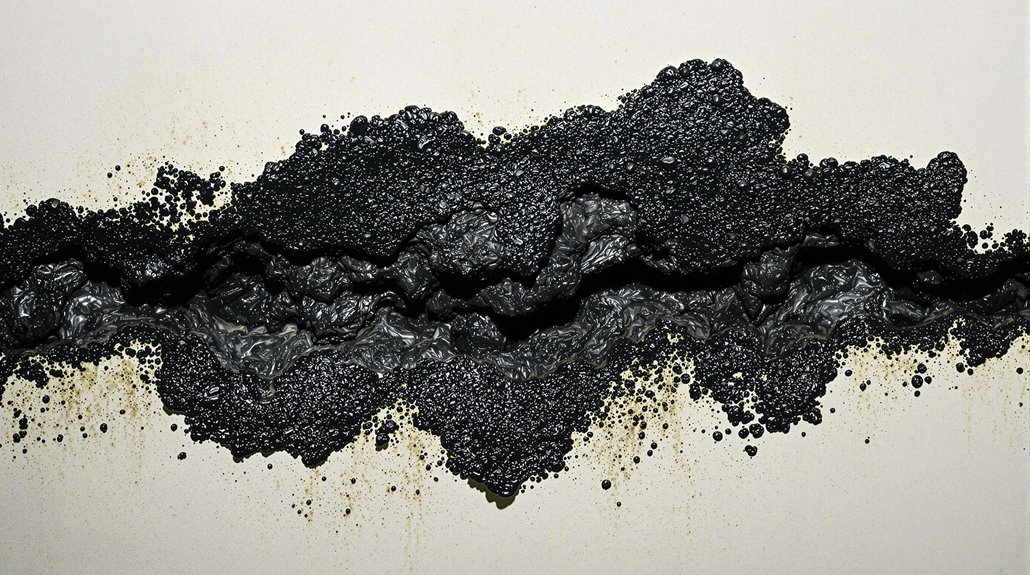

Distinguishing between black mold and mildew is key to addressing a potential infestation effectively. The primary difference lies in their appearance and characteristics.
Black mold, typically identified as *Stachybotrys chartarum*, appears as dark green or black patches with a wet, slimy texture. In contrast, mildew is usually seen as gray or white powdery spots on surfaces.
Mold penetrates deeper into materials, causing structural damage, while mildew grows mostly on the surface, making it easier to clean. Additionally, mildew emits a musty odor, whereas black mold produces a stronger, more pungent smell.
Health risks also vary, with black mold posing greater risks, especially to individuals with respiratory conditions. Understanding these differences is essential for effective remediation and mitigation of health issues.
Both types of fungi thrive in bathrooms with poor ventilation practices and humidity levels above 50%.
Black Mold Growth and Appearance
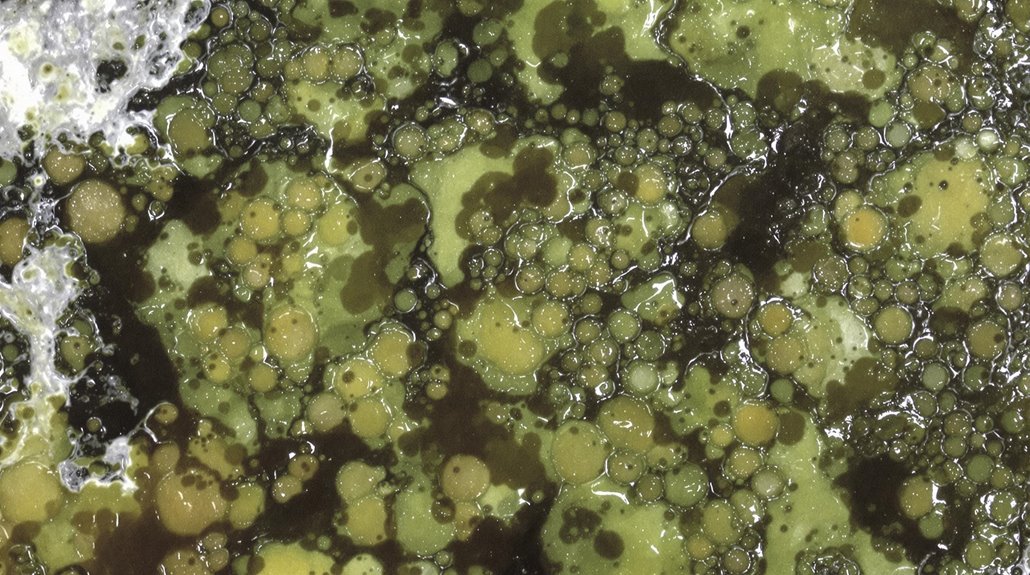
As black mold begins to colonize a surface, its growth pattern and appearance can provide essential clues to its identity. Black mold typically thrives in humid conditions, feeding on cellulose-rich materials found in common household items.
The appearance of black mold can vary, but distinct characteristics include a wet, slimy texture and fuzzy edges.
Key identifying features of black mold growth include:
- Dark Green, Brown, or Black Coloration: Visible signs of black mold can range from dark green to brown or black, often accompanied by a fuzzy white edge.
- Clusters of Circular Spots: Black mold commonly grows in clusters, with spots developing a fuzzy edge during the active growth phase.
- Musty Odor: A distinct musty smell, similar to wet soil or decay, is often produced by black mold, aiding in its identification even without visible growth. This odor is a result of the release of black mold spores.
When relative humidity reaches above 70 percent, black mold can rapidly colonize and spread throughout affected areas.
Common Areas for Black Mold Growth

Black mold growth is often linked to specific areas within a building where moisture accumulates and ventilation is poor.
Basements, bathrooms, and kitchens are common areas prone to high moisture levels, making them ideal environments for black mold to thrive.
Poor ventilation in these areas exacerbates the issue, allowing black mold to develop on cellulose-rich materials such as drywall, wood, and paper.
Behind appliances, under sinks, and around windows are also prime locations for black mold growth due to condensation.
Water damage from leaks or flooding can further create an environment conducive to black mold development, particularly if not addressed promptly.
Visible patches of black or dark green mold and a musty odor are common indicators of black mold presence.
Understanding these common areas for black mold growth is essential in preventing its development and mitigating potential issues.
Regular inspections and prompt remediation are key to controlling black mold.
These areas typically maintain 70 percent humidity levels which create optimal conditions for rapid mold development.
Health Effects of Black Mold Exposure
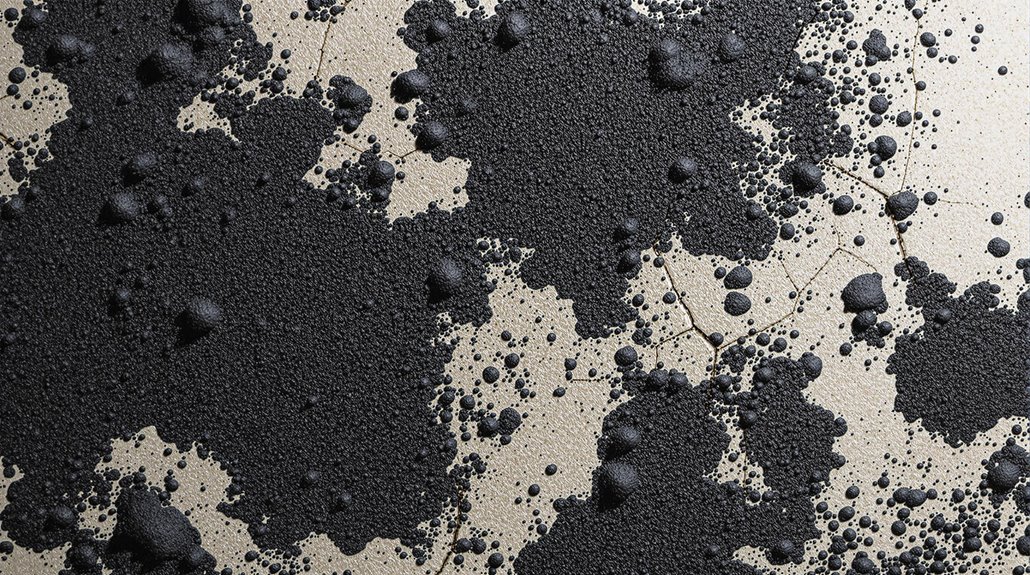

Exposure to toxic mold species, particularly in indoor environments, poses significant health risks to humans. The health effects of black mold exposure can be severe, particularly for individuals with weakened immune systems.
The following health issues can arise from exposure to black mold:
- Respiratory problems: Coughing, sneezing, and nasal congestion can occur in sensitive individuals, while prolonged exposure can exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Allergic reactions: Immediate reactions, including skin rashes and red eyes, can occur in individuals with mold allergies.
- Serious health issues: High concentrations of black mold can lead to neurological symptoms, such as headaches and dizziness, while vulnerable populations may experience respiratory infections and chronic health conditions.
Brain fog and memory problems frequently develop due to mycotoxin exposure in water-damaged buildings.
Prolonged exposure to black mold can lead to serious health issues, including fungal infections.
It is crucial to recognize the health effects of black mold exposure to prevent long-term damage and guarantee a safe indoor environment.
Removing and Preventing Black Mold
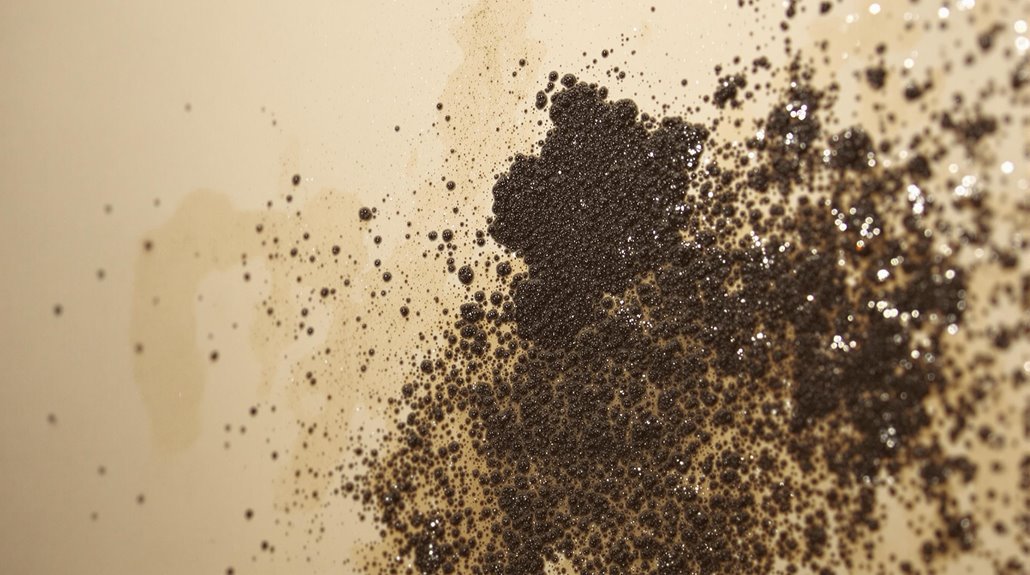

Numerous strategies can be employed to remove and prevent black mold growth in indoor environments.
When removing black mold, it is essential to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and masks to avoid inhaling spores and protect the skin. A mixture of bleach and water or white vinegar can be used to scrub moldy surfaces, ensuring the area is well-ventilated during cleaning.
For prevention, maintaining indoor humidity between 30% and 50% is vital, using dehumidifiers and exhaust fans in moisture-prone areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Immediately addressing any water leaks and water damage can greatly reduce the risk of black mold growth.
Effective removing and preventing measures can mitigate the health risks associated with black mold exposure. By controlling humidity and promptly addressing water damage, individuals can prevent a mold problem from arising and minimize the need for costly and time-consuming removal efforts.
The Benefits Of Consulting A Public Adjuster

When evaluating and addressing black mold damage, policyholders can benefit greatly from consulting a public adjuster.
These professionals bring expertise in insurance claims, providing an objective damage evaluation and streamlining the claim process to guarantee fair compensation.
Expertise In Insurance Claims
A crucial step in traversing the complexities of insurance claims for black mold damage is consulting a licensed public adjuster. Public adjusters possess expertise in interpreting insurance policies and understanding coverage limits, leading to more accurate and successful claims outcomes.
Their expertise in insurance claims includes:
- Thorough damage assessments: Conducting detailed evaluations to identify all areas affected by mold damage.
- Effective claim documentation: Gathering and presenting evidence to substantiate claims and guarantee fair settlements.
- Insurance policy interpretation: Understanding coverage limits and policy provisions to maximize compensation for policyholders.
Objective Damage Assessment
Public adjusters play an essential role in securing fair insurance settlements for black mold damage claims, and their expertise extends beyond interpreting insurance policies. A public adjuster can provide an objective damage assessment, utilizing industry-standard tools and methodologies to accurately document the extent of damage. This may include moisture mapping and air quality testing, providing evidence-backed reports for your insurance company.
| Benefits of Public Adjuster | Methods Used | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Thorough damage assessment | Moisture mapping | Accurate documentation of damage |
| Industry-standard tools and methodologies | Air quality testing | Evidence-backed reports for insurance company |
| Increased likelihood of successful claim | Professional representation | Higher compensation amounts |
| Time and stress savings | Negotiations with insurance providers | Focus on mold remediation and removal |
| Mitigation of health problems | Assisting in chronic fatigue prevention | Improved overall well-being |
Streamlined Claim Process
While maneuvering through the complexities of a black mold damage claim can be an intimidating task for policyholders, consulting a public adjuster can greatly streamline the process. A public adjuster's expertise in insurance policies and claims procedures enables them to effectively navigate complex situations, avoiding pitfalls that could hinder a claim.
The benefits of consulting a public adjuster include:
- Accurate Documentation: Ensuring all necessary documentation is accurately prepared and submitted, reducing delays in approval by insurance companies.
- Expert Advocacy: Advocating for a fair settlement and securing higher claims than the insured would achieve on their own.
- Time and Stress Savings: Handling negotiations and communications with the insurance company, allowing the homeowner to focus on recovery and taking steps to remove mold, help prevent its return, and prevent black mold's common exposure that causes health issues, including respiratory issues when one breathes in black mold.
Higher Claim Payouts & Settlements
Maximizing insurance claim payouts is a key advantage of consulting a public adjuster. Public adjusters assess the full extent of damage, providing detailed documentation that can lead to higher settlements. On average, homeowners who work with public adjusters receive settlements 20-30% higher than those who handle claims without professional assistance.
| Benefits of Public Adjusters | Homeowner Impact | Insurance Company Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed damage assessment | Higher claim payouts | Expert negotiation |
| Identification of coverage options | Increased settlement amounts | Direct communication |
| Expedited claims process | Faster resolution | Reduced stress |
| Expertise in policy language | Accurate claim filing | Compliance with regulations |
About The Public Claims Adjusters Network (PCAN)

As the insurance claims landscape continues to evolve, the Public Claims Adjusters Network (PCAN) has emerged as an essential resource for policyholders seeking expert guidance and representation.
PCAN is a national network of pre-vetted, verified, and state-licensed public adjusters who specialize in residential and commercial property damage insurance claims, including those related to mold and its impact on health.
The following key aspects of PCAN's services are significant:
- Expert Representation: PCAN member adjusters are considered the best-of-the-best, with expertise in over 30 different claim types, guaranteeing policyholders receive expert guidance and representation.
- Rigorous Vetting Process: Member adjusters must undergo an intensive application and interview process, ensuring they meet the highest standards of ethics, morals, and professionalism.
- Nationwide Coverage: With member adjusters located in 40+ states, PCAN provides policyholders with access to expert resources, regardless of location, to navigate complex insurance claims and guarantee fair settlements for property damage, including mold-related claims.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can You Tell if You Have Black Mold?
"When in doubt, check it out" holds true for black mold identification. Look for mold growth signs, high indoor humidity levels, and moisture sources. Visual inspection techniques, mold testing kits, and health symptoms can also confirm its presence.
How Harmful Is Black Mold to Humans?
Black mold poses significant health risks to humans, triggering respiratory issues, allergy symptoms, and skin irritation, particularly in individuals with weakened immune responses or chronic conditions, emphasizing the need for effective prevention methods and remediation techniques.
Is It Safe to Stay in a House With Black Mold?
"When in doubt, get out" applies to black mold exposure. Staying in a house with black mold poses significant health risks, including respiratory issues and neurological problems, emphasizing the need for professional testing, removal, and prevention to mitigate long-term effects.
What Can Be Mistaken for Black Mold?
Black mold can be mistaken for other mold types, including green mold, white mold, brown mold, and yellow mold. Proper mold identification requires examination of mold characteristics, and incorrect identification can complicate mold removal and prevention efforts.








